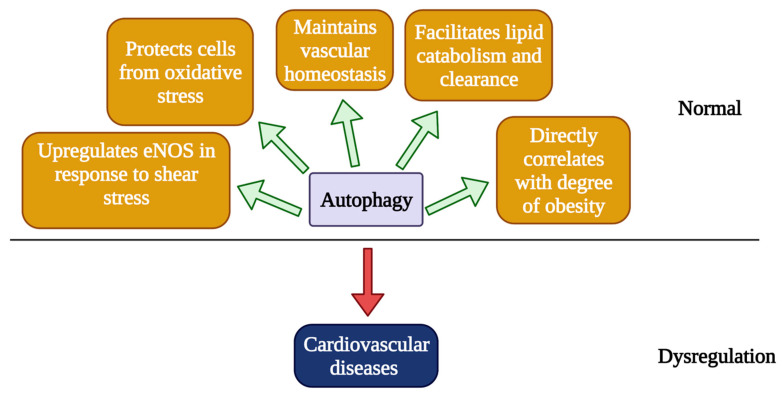
Figure 2.
Roles of autophagy in the pathobiology of cardiovascular diseases. Autophagy is essential for regulating endothelial functions to maintain vascular homeostasis. Autophagy plays an important role in lipid clearance, and impaired autophagy leads to the accumulation of lipid, which is a known risk factor for the development of atherosclerosis. Mitophagy can protect vascular ECs from oxidative stress by removing damaged mitochondria and by preventing the elevation of ROS. Shear stress in the vessel wall can induce autophagy, which resulted in reduced ROS and increased NO production, mainly by upregulating eNOS and increased cell viability. Autophagy correlates with the level of obesity, a major risk factor for developing CVDs. Dysregulated autophagy can lead to CVDs, which will be discussed in detail in the next section.