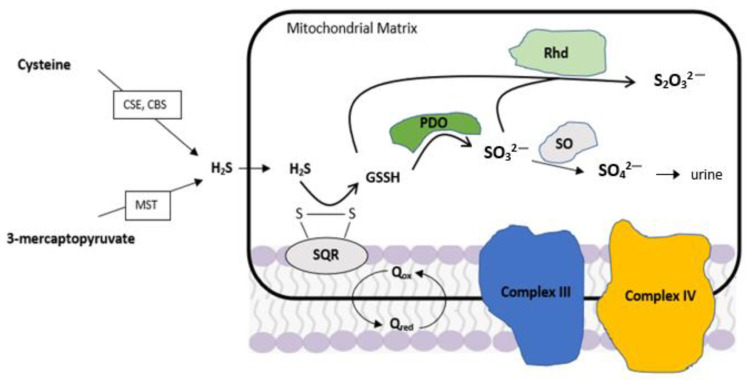
Figure 1.
Generation of thiosulfate from H2S in the mitochondrial sulfide oxidation pathways. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) is produced by enzymes cystathione γ-lyase (CSE) and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) in the trans-sulfuration pathway. A third enzyme, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MST), also produces endogenous H2S in the presence of the substrate 3-mercaptopyruvate. A membrane-bound sulfide, quinone oxidoreductase (SQR), oxidizes H2S to persulfide, which is transferred to a glutathione (GSH). A persulfide dioxygenase (PDO) in the mitochondrial matrix oxides one glutathione persulfide (GSSH) to sulfite (H2SO3), which is then used in a sulfurtransferase reaction catalyzed by the enzyme rhodanase (Rhd) to form thiosulfate (S2O32−) by transferring a second glutathione persulfide from SQR to sulfite. Sulfite can be further oxidized by sulfite oxidase (SO) to form sulfate (SO42−) and is subsequently excreted in urine. PDO and SO are oxygen dependent enzymes.