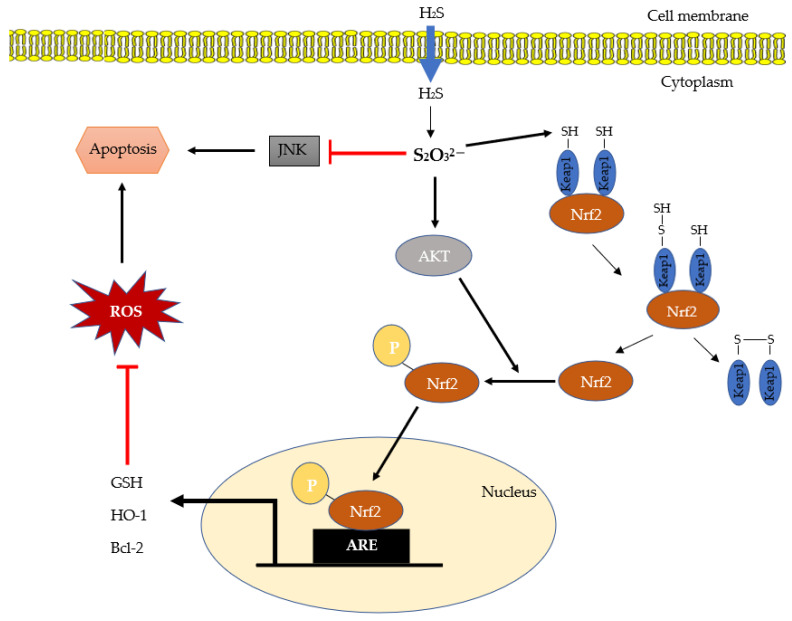
Figure 2.
Proposed overview of cytoprotective effects of thiosulfate against oxidative stress. Thiosulfate (S2O32−) is produced from hydrogen sulfide (H2S) via sulfide oxidation pathway. The bound sulfur on thiosulfate activates the Nrf2 system through the structural change of Keap1 proteins and induction of phosphorylated AKT. The nuclear translocation of phosphorylated Nrf2 binds to ARE to promote expression of various antioxidative gene clusters. Thiosulfate also contributes to anti-apoptotic signaling via inhibition of JNK phosphorylation. ROS, reactive oxygen species; GSH, glutathione; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; ARE, antioxidant response element; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; AKT, protein kinase B; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases.