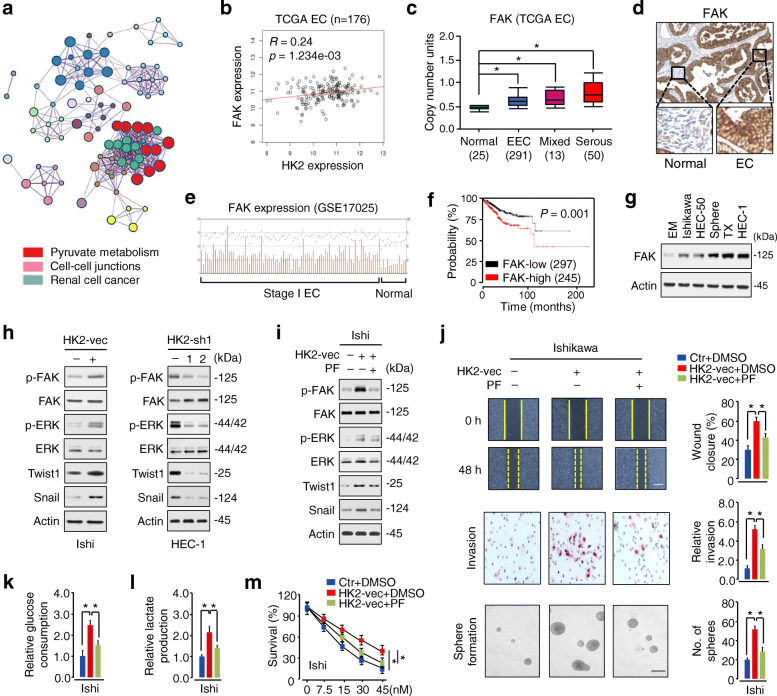
Fig. 3.
HK2 initiates EMT and enhances glucose metabolism in EC cells by activating the FAK/FAK/ERK1/2 pathway and upregulating Twist1 and Snail expression. a The top 100 genes that show a positive or negative co-expression correlation with HK2 in the TCGA EC dataset were selected and uploaded to Metascape for GO term detection and clustering. Same-colored dots fall into a function similar to the given title. Only the top 20 significant GO categories were shown. b Pearson correlation analysis revealed that HK2 was significantly correlated with FAK in the TCGA EC dataset using LinkedOmics. c Analysis of FAK levels in EC and normal tissues using the TCGA data from UALCAN. d The protein expression of FAK in EC and adjacent normal tissues. Images were downloaded from Human Protein Atlas. e The microarray dataset (GSE17025) was analyzed for FAK expression in stage I EC samples and normal endometrium samples. f Kaplan-Meier curves show the overall survival of EC patients with high or low FAK expression from KM Plotter. g Western blotting analysis of FAK expression in a normal endometrial cell line (EM) and human EC cell lines, including Ishikawa, HEC-1, HEC-50, and sphere-forming (sphere) or TX-resistant (TX) HEC-50 derivatives. h Western blotting analysis of the indicated proteins in EC cells following overexpression or knockdown of HK2. i Western blotting analysis of the indicated proteins in Ishikawa cells expressing HK2, in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor PF-573,228 (PF). j, k, l Cell migration, invasion, sphere formation, glucose consumption, and lactate production of Ishikawa cells expressing the control vector or HK2 vector, in the presence or absence of FAK inhibitor PF. m Ishikawa cells were transfected with or without the HK2 vector and treated with TX. Cell survival was examined by a cell viability assay in the presence or absence of PF. Ishi: Ishikawa; vec: vector; sh: shRNA. *P < 0.05