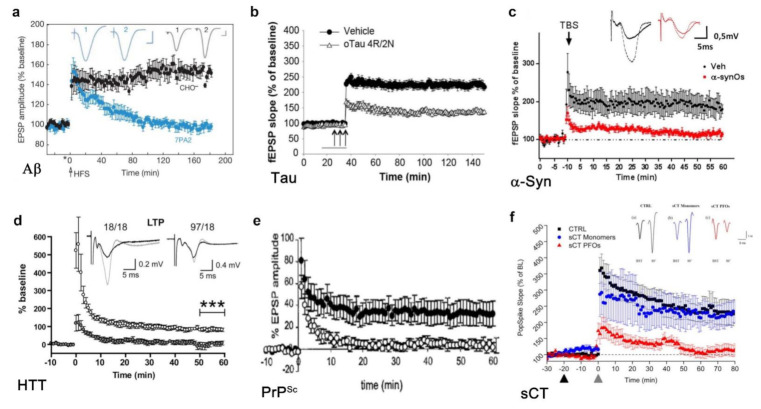
Figure 3.
Reduction in LTP observed in models for the study of the amyloid neurotoxicity. (a) Alzheimer’s disease: microinjection of Aβ oligomers (blue) strongly reduced hippocampal LTP compared to control (black) (with the courtesy of Walsh et al. [178]); (b) Alzheimer’s disease: perfusion with tau oligomers (white) impairs LTP in mouse hippocampal slices (with the courtesy of Fá et al. [179]); (c) Parkinson’s disease: α-syn oligomers (red) reduce LTP in the CA1 region in mouse hippocampal slices (with the courtesy of La Vitola et al. [180]); (d) Huntington’s disease: hippocampal LTP recorded in the CA1 region of hippocampal slices from 9-month-old Hu97/18 model mice (black) is significantly reduced compared with that of animals of the same age (white) (with the courtesy of Kolodziejczyk et al. [177]); (e) prion disease: mice infected with scrapie ME7 shows a strongly reduced LTP in the CA1 area (white) (with the courtesy of Johnston et al. [181]); (f) amyloid model: treatment with sCT PFOs (red) results in impairment of LTP in mouse hippocampal slices while slices treated with monomeric sCT (blue) show no significant changes compared to control (black) (with the courtesy of Belfiore et al. [25]).