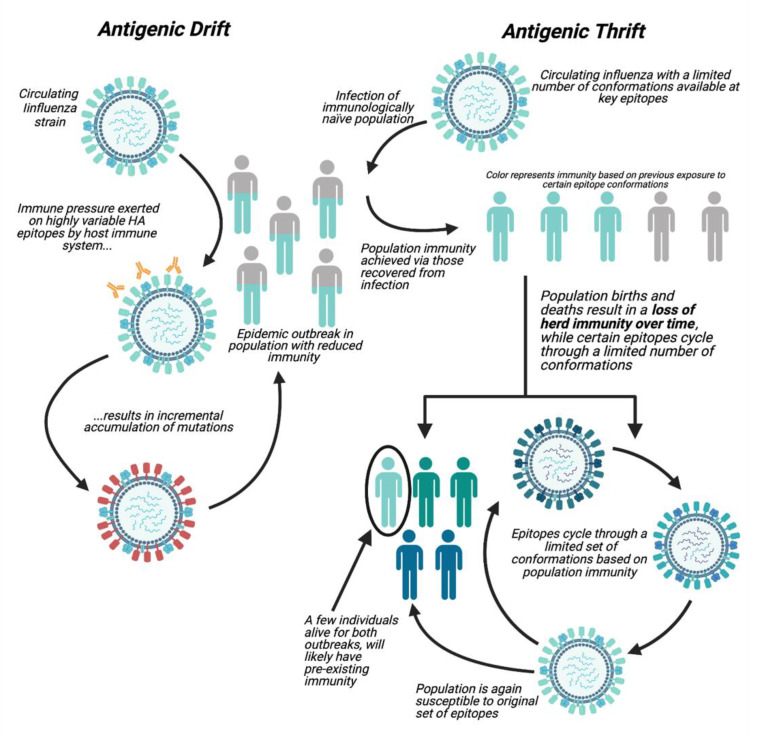
Figure 2.
A comparison of the antigenic drift and thrift theories. Antigenic drift theory states that influenza is highly variable and escapes population immunity through the accumulation of incremental mutations over time. Conversely, the antigenic thrift theory states that population immunity is directed against epitopes of limited variability (ELVs) [31,44]. Population immunity to these ELVs changes over time due to births and deaths in a population. This allows for the reappearance of historical strains once immunity against them has waned.