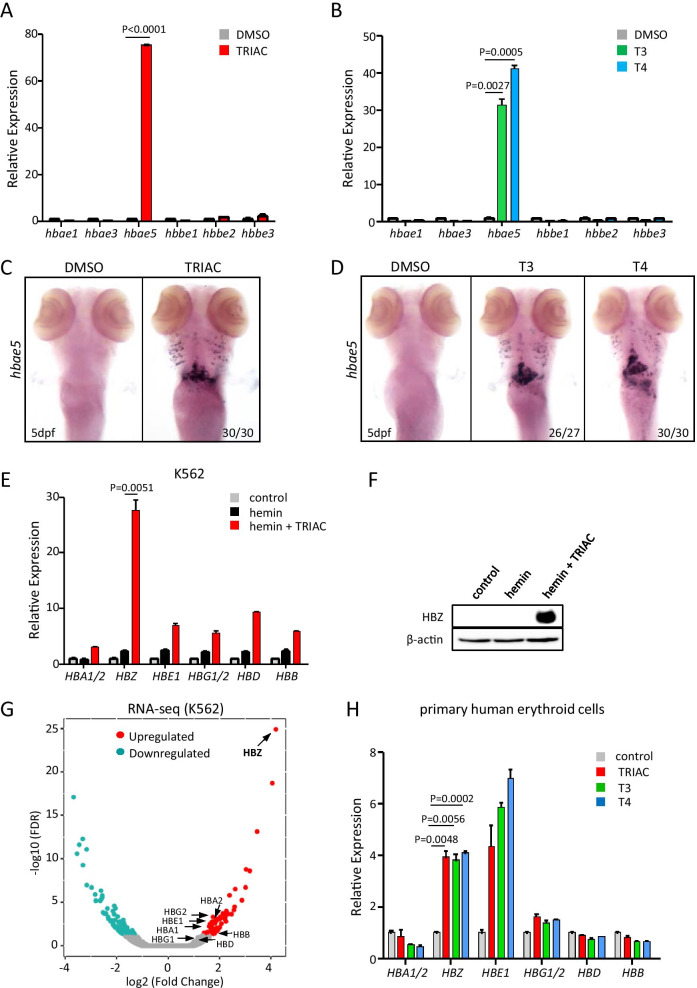
Fig. 1.
Thyroid hormones induce ζ-globin expression. A, B qPCR was performed on RNA from the TRIAC, T3- or T4-treated zebrafish embryos at 5 dpf and normalized to the level of zebrafish β-actin. Data shown are the means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student’s t test. C, D WISH assay of hbae5 shows TRIAC, T3- or T4-induced ζ-globin gene expression in zebrafish embryos at 5 dpf, respectively. dpf, days post-fertilization. E TRIAC induced ζ-globin production in hemin-treated K562 cells. qPCR was performed after 48 h of incubation with TRIAC, and normalized to the level of human β-actin. Data shown are the means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student's t test. F Western blots of lysates of TRIAC-treated K562 cells. G Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in TRIAC-treated K562 cells compared with control cells. Globin genes are indicated by arrows. FDR, false discovery rate. H Thyroid hormones induced ζ-globin gene expression in primary human erythroid cells. Human CD34+ cells were induced into an erythroid lineage and treated with TRIAC, T3 or T4, respectively. The total RNAs were isolated on day 7 of differentiation and subjected to qPCR analysis. Data shown are the means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student’s t test