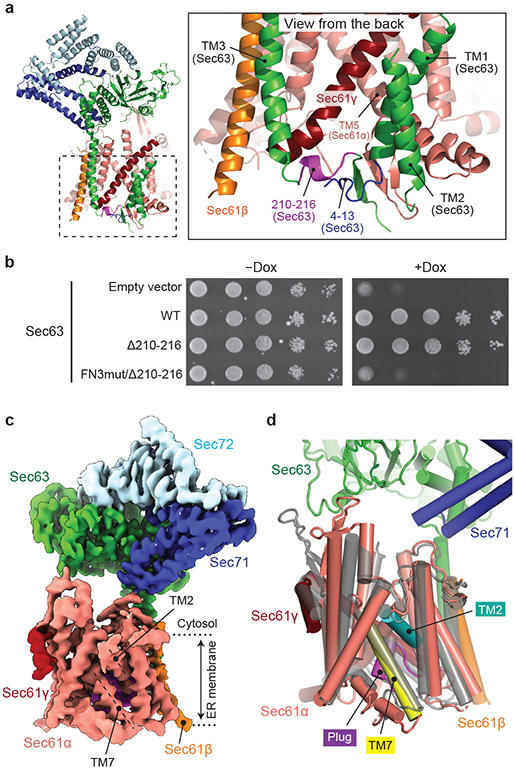
Figure 5. The structure of a fully closed Sec complex.
a, The interaction between Sec61 and Sec63 in the ER lumen (view from the back). The N-terminal segment (positions 4–13) and the segment preceding TM3 (positions 210–216) of Sec63 are in blue and purple, respectively. Shown is the ScSec[C1] structure. b, Yeast growth complementation (at 30°C) testing functionality of the indicated Sec63 mutants. The addition of doxycycline (Dox) represses chromosomal WT Sec63 expression. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results. c, The 3.8-Å-resolution cryo-EM structure of the ScSec complex containing FN3mut/Δ210-216 double-mutant Sec63. The lateral gate helices TM2 and TM7 are indicated. d, As in c, but showing the atomic model of the Sec61 complex. For comparison, the closed M. jannaschii SecY structure (PDB 1RH5; semitransparent grey) is superimposed.