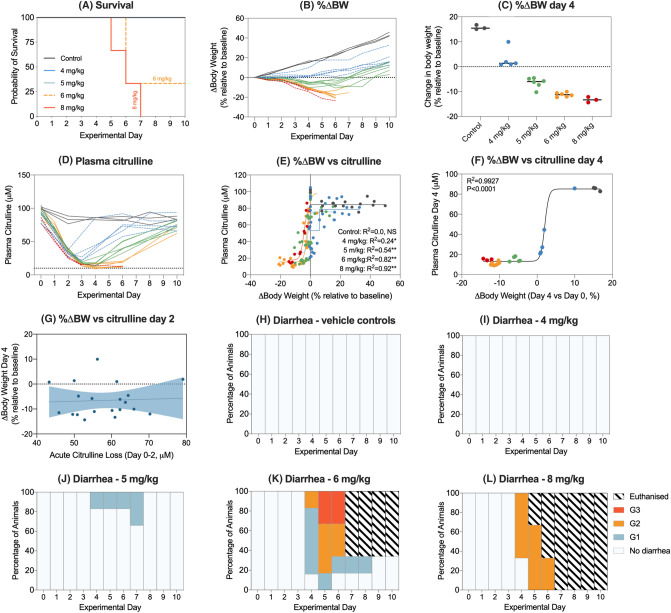
Fig. 1.
Dose finding study. To determine the optimal dose of melphalan, rats were treated with 4, 5, 6, and 8 mg/kg intravenous melphalan and clinical measures of gastrointestinal mucositis assessed for 10 days. Doses of 6 and 8 mg/kg caused unaccepted morbidity and mortality (a/b). 5 mg/kg melphalan-induced moderate, self-limiting disease. Weight loss at day 4 was dose-dependent (c) and correlated with plasma citrulline (d–f). Hypocitrullinemia in first 2 days after melphalan was independent of dose and did not correlate with acute weight loss (g). Diarrhea severity was dose-dependent (h–l). Non-linear regression analyses with Pearson’s correlation analysis was performed for all association plots