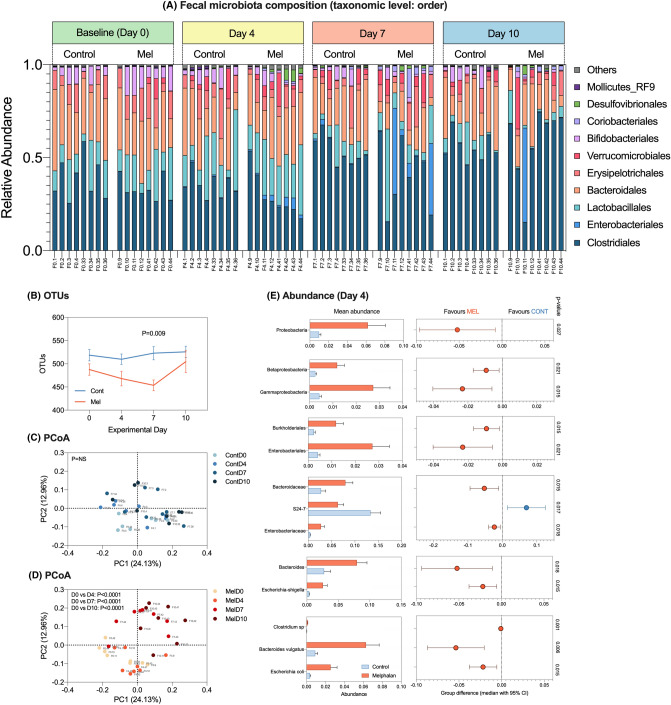
Fig. 5.
Melphalan-induced dysbiosis is characterized by expansion of enteric pathogens. Panel a showed relative abundance for individual animals assessed longitudinally over experimental time course. Data are shown at taxonomic level of order. OTUs were significantly decreased at day 7 post-melphalan (b), with principle component analyses demonstrating significant shifts in the microbiota post-melphalan that were unable to resolve (c–d). Panel e shows significantly altered taxa (mean ± SEM) at day 4 and median difference between groups (median ± 95% CI)