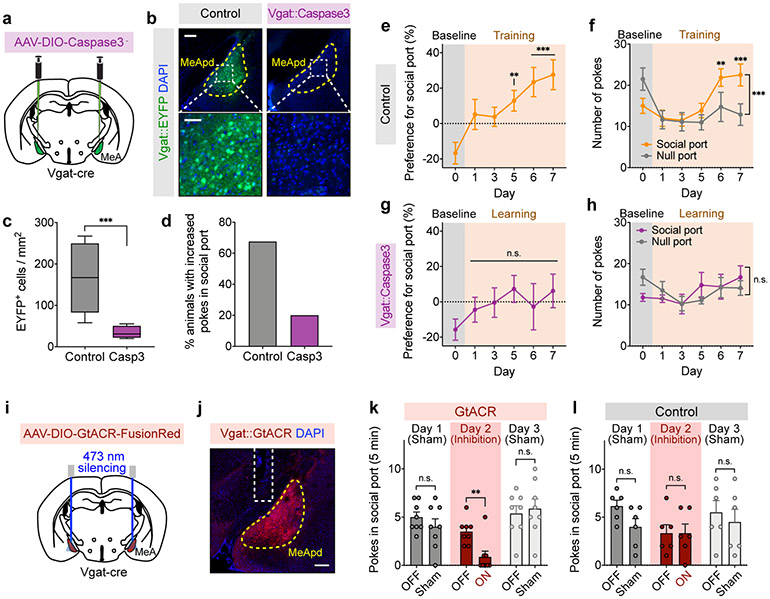
Figure 2. MeApd Vgat+ neurons are required for social reward.
a, Schematic of viral injection for cell type-specific ablation. b, Representative images of MeApd Vgat+ neurons (labeled by EYFP) in control and caspase-3-expressing animals. Top images, scale bar = 200 μm; bottom images, scale bar = 50 μm. c, Quantification of EYFP-expressing Vgat+ neurons in control and caspase-3-expressing animals. Cell type-specific ablation substantially reduced Vgat+ neurons in the MeApd. ***P < 0.0001, Mann-Whitney test (two-sided). d, Fractions of animals that exhibit a consistent preference for social port in control or caspase-3-expressing animals. e, g, Caspase-3-expressing animals (g), but not control (e) ones, fail to develop preference for social port during the training session. One-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc correction (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). f, h, Number of pokes of social and null ports with target animals across days. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc correction (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). i, Schematic of viral injection for optogenetic inhibition. j, A representative image showing the expression of GtACR-FusionRed in MeApd Vgat+ neurons. Scale bar = 200 μm. k, l, Optogenetic silencing of MeApd Vgat+ neurons in GtACR-expressing (k), but not control (l), animals significantly reduces pokes in social port in the social operant task. After animals established a positive preference for social port, sham inhibition was performed on days 1 and 3, while optogenetic inhibition was performed on day 2. In (b-h), n = 10 mice (Caspase-3) and 8 mice (control). In (j-l), n = 8 mice (GtACR) and 6 mice (control). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc correction (**P < 0.01). (c) boxplots: center = median, box = quartiles, whisker = 10–90 percentile; (e-h, k, l), mean ± SEM. For detailed statistics information, see Supplementary Table 1.