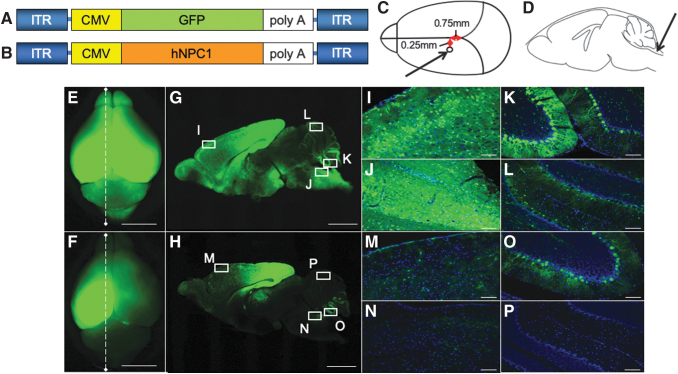
Figure 1.
Broad transduction of the brain by AAV-GFP vector. We generated the tyrosine-mutant AAV9/3 vector with CMV promoter. (A), (B) An illustration of the vector constructs. The expression cassette consisting of CMV promoter, cDNA of GFP or hNPC1, and simian virus (SV) 40 poly A were inserted between the inverted terminal repeat (ITR) of AAV3. Capsids were tyrosine-mutant AAV9. The vectors were prepared at a titer of 1.8 × 1010 vg/μL. (C) Five microliters of twofold diluted AAV-GFP vector was injected into the left ventricle. The stereotaxic coordination was 0.75 mm anterior from the lambdoid suture and 0.25 mm left from the center, and 2 mm deep from the surface of the skull. (D) Ten microliters of AAV-GFP was injected into the cisterna magna. The total injection dosage was 15 μL (1.35 × 1011 vg) per mouse. Arrows indicate the positions of the injection. A distribution analysis of the GFP vector in the brain at 3 weeks after the injection of AAV-GFP vector. E and F are whole-brain GFP fluorescent images obtained by a stereomicroscope. G and H are sagittal sections of E and F, respectively. (E, G) Both cerebral hemispheres showed strong signals. Milder signals were observed in the cerebellum. (F, H) In this mouse, we injected 5 μL of AAV-GFP vector only into the left ventricle. Strong signals in the left hemisphere and slight signals in the right hemisphere were observed, but fewer signals were noted in the cerebellum. Higher magnification of the frontal cortex (I, M), brain stem (J, N), lower part of the cerebellum (K, O), and upper part of the cerebellum (L, P) was shown. Strong signals were detected in I, J, and K, compared with M, N, and O. In L, the signal was weakly observed. Scale bar = 5 mm (E, F), 2 mm (G, H), 100 μm (I–P). AAV-GFP, adeno-associated virus-green florescent protein; CMV, cytomegalovirus; hNPC1, human Niemann–Pick type C1 gene.