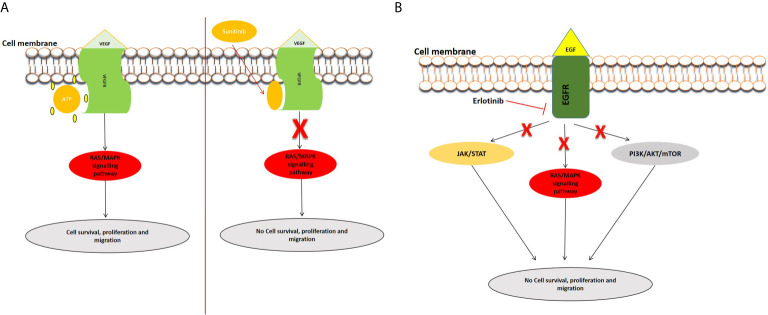
Figure 1.
Examples of inhibition of the VEGFR and EGFR signaling pathways. (A) Inhibition of VEGFR signal transduction by sunitinib. After the entry of sunitinib into the cytoplasm, it competitively binds at the ATP site of VEGFR, consequently inhibiting the activation of the pathway. (B) Mechanism of action of Tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Erlotinib is a small molecule that acts as an ATP analogue and inhibits EGF signaling by binding to receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), and inhibits the activation of downstream signaling pathways.