Fig. 5. Protein-protein interaction-perturbing alleles in histone H4 complex.
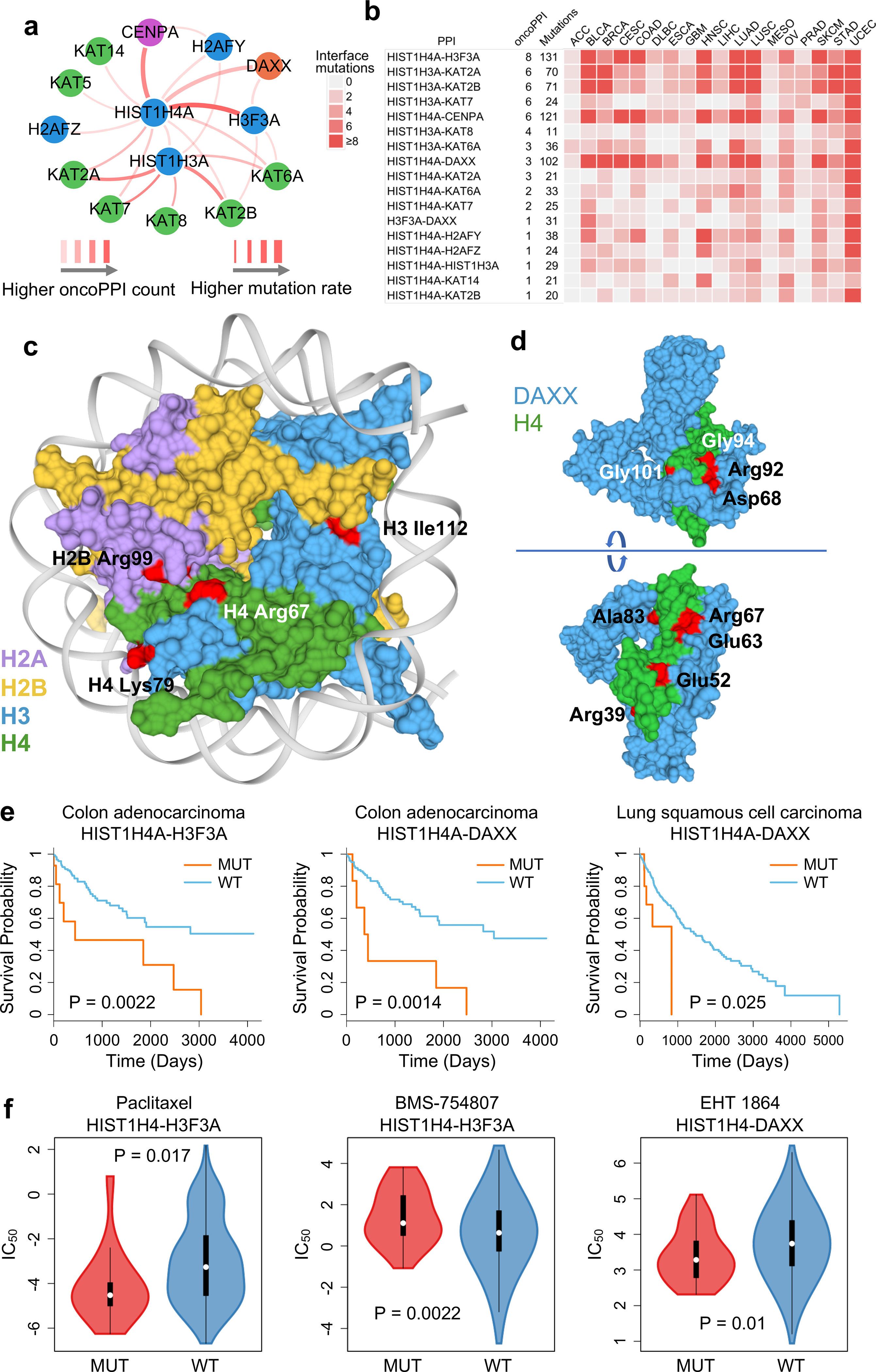
(a) A highlighted PPI-perturbing mutation network for the histone H4 complex in human cancer. (b) Somatic mutation landscape of histone H4 complex across 18 selected cancer types with the highest number of somatic mutation rate. (c) Selected PPI-perturbing mutations (highlighted by red) in histone H4 complex. (d) Interface mutations (highlighted by red) between histone H4 and DAXX. (e) Interface mutations of histone H4 complex are significantly correlated with survival in colon adenocarcinoma (COAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC). The p-value (P) was calculated by two-tailed Log-rank test. (f) Interface mutations of histone H4 complex are significantly correlated with anticancer drug responses, including paclitaxel (n=16 mutated cell lines; n=411 wild type cell lines), BMC-754807 (an IGF-1R inhibitor) (n=32 mutated cell lines; n=895 wild type cell lines), and EHT-1864 (a Rho inhibitor) (n=36 mutated cell lines; n=928 wild type cell lines). The p-value (P) was calculated by two-tailed ANOVA test. The data are represented as a boxplot with a underlaid violin plot where the middle line is the median, the lower and upper edges of the box are the first and third quartiles, the whiskers represent the interquartile range (IQR) ×1.5 and beyond the whiskers are outlier points.
