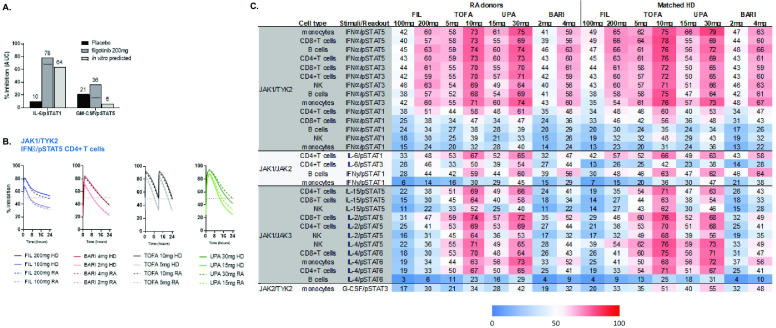
Figure 5.
Cytokine-induced pSTAT inhibition in the samples of patients with RA and in ex vivo stimulated blood from phase 1 studies of healthy volunteers. (A) Measured average inhibition of ex vivo stimulated pSTAT1 (IL-6/CD4+ T-cells) and pSTAT5 (GM-CSF/monocytes) over a 24-hour period in healthy volunteers receiving FIL (200 mg once daily) or placebo or from in vitro calculated values. The black bar indicates placebo-adjusted inhibition. FIL values include contribution of GS-829845. (B) Calculated pSTAT5 inhibition for JAKinibs at RA clinical doses over a 24-hour dose interval at steady state for IFNα/pSTAT5 in CD4+ T-cells in HDs (n=2) and patients with RA (n=3) based on in vitro measurements. (C) Heatmap of average daily percent STAT inhibition (area under the curve (AUC)–24 hours) by JAKinibs at clinical doses in patients with RA and matched HDs (based on in vitro whole blood measurements; n=2–3). BARI, baricitinib; FIL, filgotinib; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor; HDs, healthy donors; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; JAK, Janus kinase; JAKinib, JAK inhibitor; NK, natural killer; pSTAT, phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; SD, standard deviation; TOFA, tofacitinib; TYK2, tyrosine kinase 2; UPA, upadacitinib.