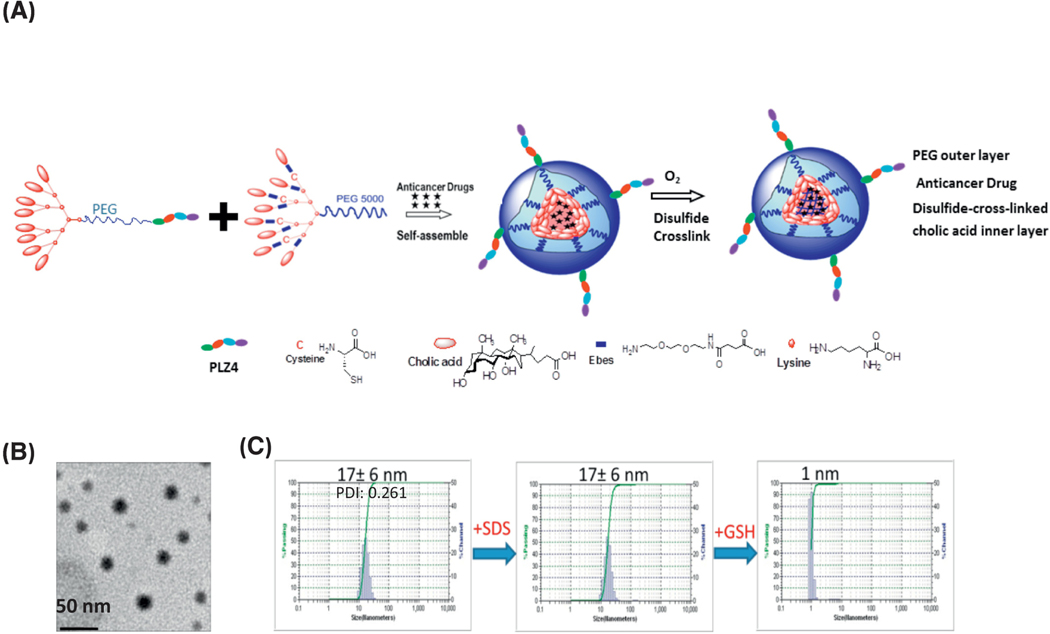
Figure 1. Synthesis and characterization of disulfide-crosslinked CLL1-targeting nanomicelles (DC-CTM).
(a) Diagram of telodendrimer and DC-CTM-DNR. Each telodendrimer (PEG5K-Cys4-L8-CA8) contains a PEG (molecular weight 5 KDa) backbone with four cysteine (C4), eight linker (L8) and eight cholic acid (CA8) units conjugated at the distal end of PEG. CLL1-L can be conjugated at the other terminus of PEG for synthesis of DC-CTM. After DNR is loaded in the core formed by cholic acid, cysteine residues can form disulfide crosslinks under oxidative conditions. These disulfide bonds are reversible and can be broken open under the reducing intracellular environment to release the drug load locally. (b) Morphologic analysis with electron microscopy. Bar = 50 nm. (c) Size distribution of DC-CTM was analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS). The same sample was treated with SDS for 10 min and particle size was analyzed again. Later, this sample was treated with 10 mM glutathione (GSH) for 30 min followed by particle size analysis.