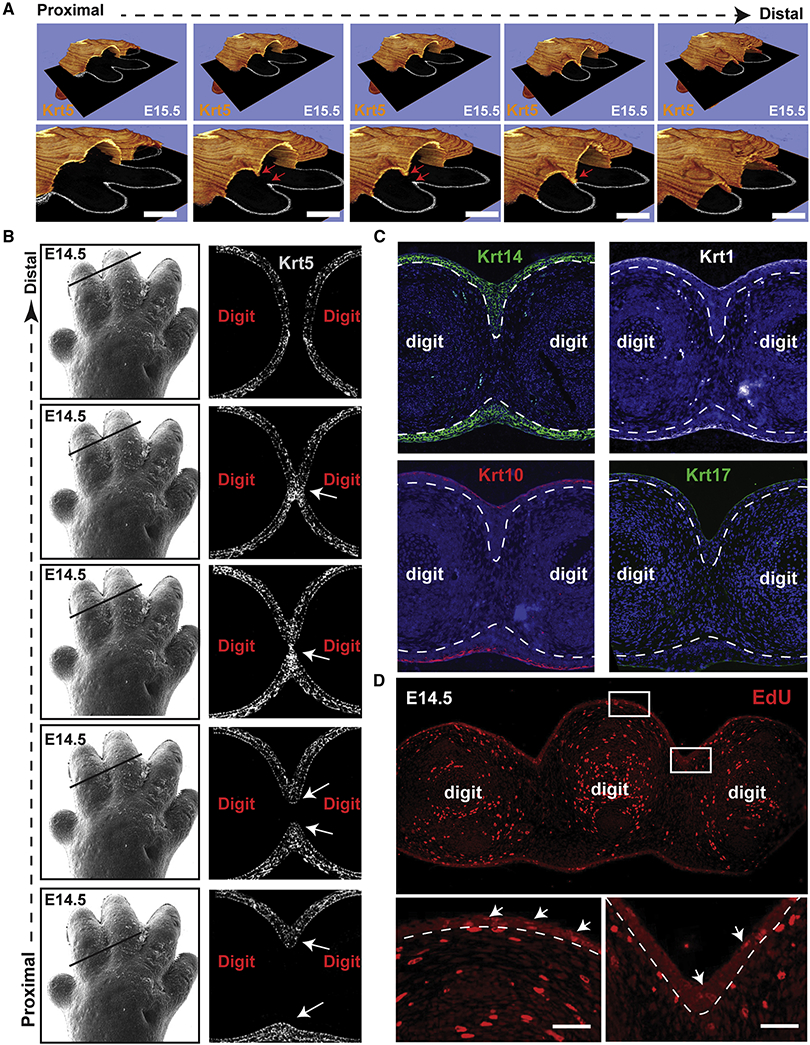
Figure 3. Formation of an interdigital epithelial tongue (IET) in normal digit separation.
(A) Series of images showing the interdigital epithelia stained with keratin-5 (orange) in continuous ortho-slices of 3D reconstructions in WT forelimbs at E15.5. Lower panels show higher magnification images. Arrows indicate the IET moving from the dorsal and ventral side. (B) left panel, scanning EM images of WT E14.5 forelimb (from figure 1). Right panel, continuous series of (proximal-to-distal) E14.5 mouse forelimb sections stained with Keratin-5 (gray). Arrows point to the IET. (C) Immunofluorescence staining showing the expression of several epithelial markers, KRT14, KRT1, KRT10 and KRT17, in the forming interdigital epithelial tongue in the E14.5 limb. (D) Proliferating cells indicated by EdU positive staining in WT forelimbs at E14.5. Arrows point to EdU positive cells in the dorsal epidermis and in the interdigital zone.