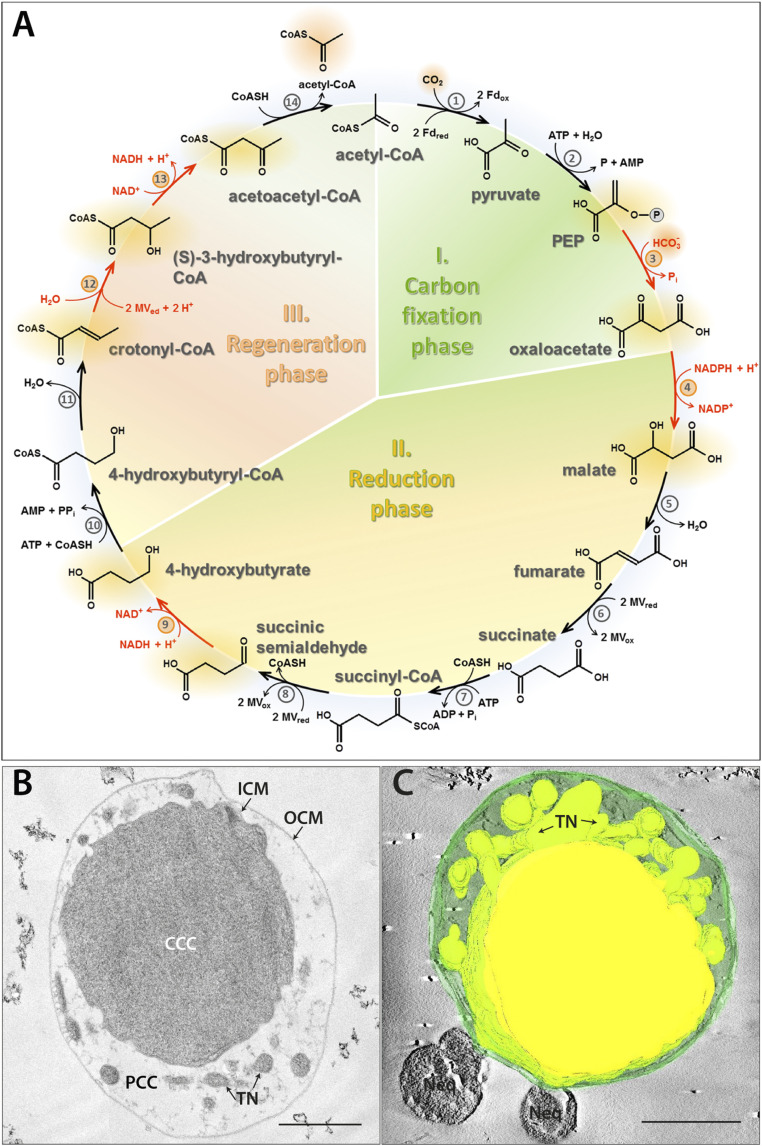
Fig. 1.
The DC/HB cycle (adapted from ref. 3) (A), ultrastructure (B), and 3D model (C) of I. hospitalis. Enzymes: 1) pyruvate synthase, 2) pyruvate:water dikinase, 3) PEP carboxylase, 4) malate dehydrogenase, 5) fumarate hydratase, 6) fumarate reductase (natural electron donor is not known), 7) succinyl-CoA synthetase, 8) succinyl-CoA reductase (natural electron acceptor is not known), 9) succinic semialdehyde reductase, 10) 4-hydroxybutyrate-CoA ligase, 11) 4-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydratase, 12) crotonyl-CoA hydratase, 13) (S)-3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, and 14) acetoacetyl-CoA β-ketothiolase. Fd, ferredoxin; MV, methyl viologen. The enzymes studied in this work are highlighted in red. Ultrathin section (B) and 3D model of a semithin section (C) of a cryo-fixed, freeze-substituted, Epon-embedded cell. CCC (central cytoplasmic compartment), PCC (peripheric cytoplasmic compartment), ICM (inner cytoplasmic membrane), TN (tubular network), OCM (outer cytoplasmic membrane), and Neq (Nanoarchaeum equitans). 3D model highlights the TN originating from the CCC. (Scale bars, 500 nm.)