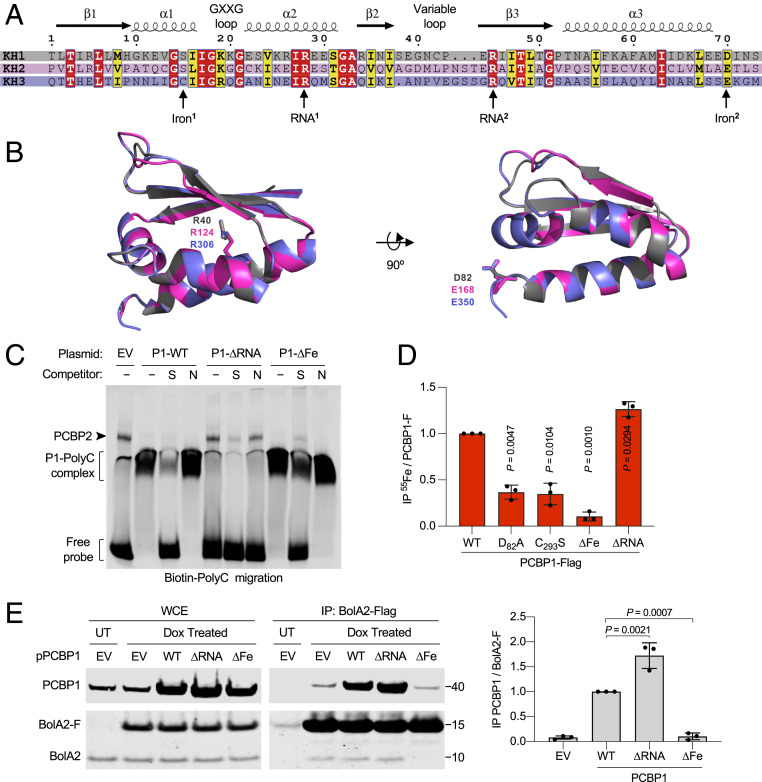
Fig. 1.
Identification of RNA- and iron-binding residues of PCBP1. (A) Sequence alignment of the three KH domains from PCBP1 illustrating secondary structure characteristics. (B) Structural comparison of three KH domains of PCBP1. Superimposed ribbon structures of KH1 (gray), KH2 (pink), and KH3 (purple) domains illustrating conserved ligands for RNA-binding (RNA1 residues: R40/R124/R306) and iron-binding (Iron2 residues: D82/E168/E350) residues as sticks. (C) Specific binding of PCBP1 variants to a poly(C) oligonucleotide probe. Biotin-labeled poly(C) oligonucleotide probe was mixed with HEK293 cell lysate transfected with EV or PCBP1-Flag (P1) variants (WT, ∆Fe: D82A/E168A/E350A, and ∆RNA: R40A/R124A/R306A) and separated by nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Specific [S, unlabeled poly(C)] or nonspecific [N, unlabeled poly(A)] oligonucleotide competitors were added, and migration of the biotin-labeled probe was analyzed by immunoblot using streptavidin-labeled antibody. (D) Requirement of iron-binding ligands for 55Fe binding to PCBP1. HEK293 cells were transfected with PCBP1-Flag WT, KH1 mutant (D82A), KH3 mutant (C293S), ∆Fe mutant, or ∆RNA mutant plasmids and labeled with 55FeCl3 for 16 h. Whole-cell extracts (WCE) and anti-Flag immune complexes were analyzed by immunoblot and scintillation counting. Specific (PCBP1-F) 55Fe binding was normalized to whole-cell 55Fe content and expressed relative to WT control. (E) Interaction of iron-binding PCBP1 variants and BolA2 in cells. Tetracycline-inducible stable cell lines expressing BolA2-Flag (BolA2-F) were transfected with plasmid (p), EV, or PCBP1 variants as indicated; treated overnight with buffer (UT) or doxycycline (Dox); and performed using anti-Flag IP. WCE and immune complexes were analyzed by immunoblot using antibodies for PCBP1 or BolA2 (Left), and the relative ratio of coprecipitated PCBP1 to BolA2-F in IP was quantified (Right). Data are means ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Significant P values, as determined by one-way ANOVA and unpaired t tests with Welch’s correction, are shown.