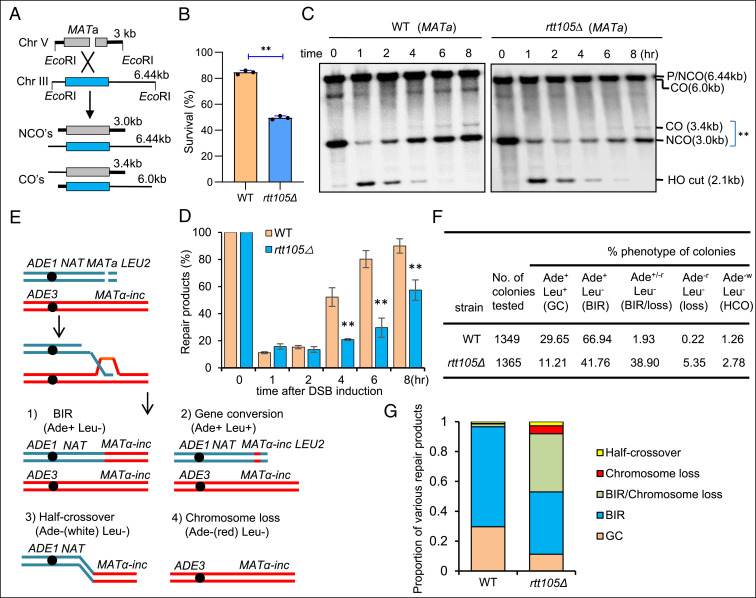
Fig. 1.
Rtt105 promotes DSB repair by gene conversion or BIR. (A) Scheme showing an ectopic recombination system. CO: crossover; NCO: noncrossover. (B) Survival rate for the WT and rtt105Δ cells repaired by ectopic recombination. (C) Southern blot analysis of the repair kinetics for indicated cells. ** marks the repair products. DSB was induced by the addition of 2% galactose to log phase cells (∼1 × 107/mL) cultured in liquid YP-Raffinose media. The samples were taken at indicated time points after DSB induction. The blot was hybridized to the MATa probe. (D) Quantification of repair products in C. The error bars in B and D represent SD from at least three independent experiments. The asterisk denotes statistical significance. **P < 0.01 (Student’s t test). (E) Diagram showing a site-specific BIR system. Repair of DSBs by different mechanisms generates distinct repair products that can be determined by following the markers on the chromosomes. (F) Repair outcomes in the WT and rtt105Δ cells. GC: gene conversion, HCO: half-crossover. Cells cultured in the preinduction liquid media were plated on YEP-Galactose media to induce DSBs. Colonies were then replica plated on Leu− or Ade− dropout media. The frequencies of BIR, half-crossover, gene conversion, and chromosome loss were calculated based on the percentage of colonies carrying markers specific for these repair outcomes. (G) Graph showing the proportion of each category of repair products in indicated strains. The statistical comparison of different repair outcomes between the WT and rtt105Δ cells in G was performed with χ2 test. P < 0.01.