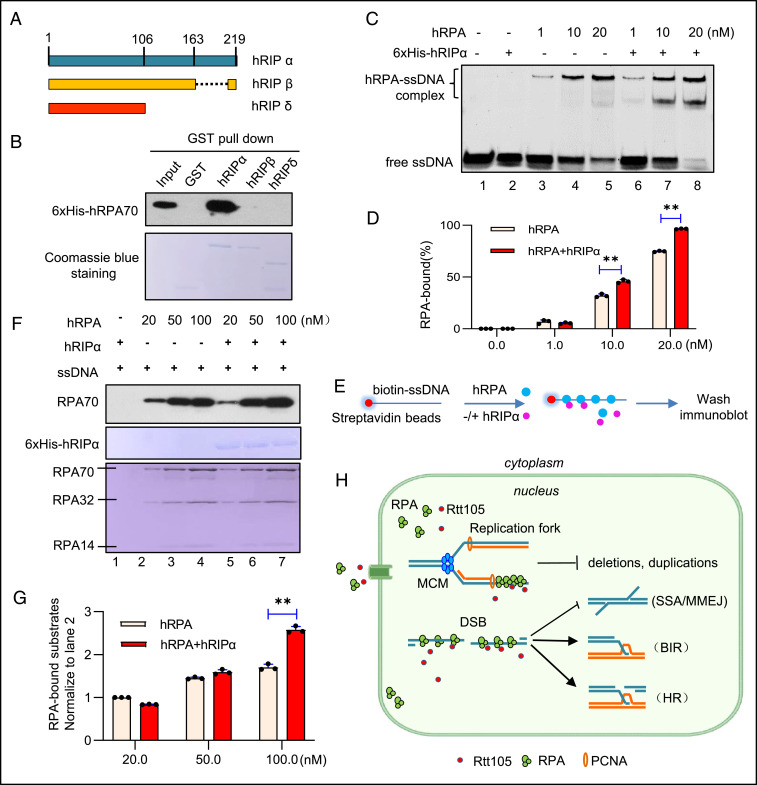
Fig. 6.
Human hRIP-α interacts with RPA and promotes RPA assembly on ssDNA. (A) Scheme showing the structure of different hRIP isoforms. (B) GST pull-down assay examining the interaction between 6xHis-hRPA70 and GST-tagged hRIP isoforms. GST was used as a control. hRIP isoforms used for experiments were indicated by Coomassie blue staining. (C) EMSA showing the stimulating effect of hRIP-α (20 nM) on hRPA (1, 10, or 20 nM) assembly on ssDNA (20 nM). (D) Quantitation of the RPA-bound ssDNA in C. (E) Scheme indicating a ssDNA pull-down assay. Biotin-labeled ssDNA (30 nt) coupled to streptavidin-coated magnetic beads was used to capture hRPA in the absence or presence of hRIP-α. We used 50 nM hRIP-α, 100 nM ssDNA, and a gradient amount of hRPA (20, 50, or 100 nM) for the experiment. (F) Western blot analysis of the ssDNA pull-down products from E. hRIP-α and hRPA used for the pull-down experiment were indicated by Coomassie blue staining. (G) Quantitation of the RPA-bound ssDNA in F. (H) A wok model for the roles of Rtt105 in preserving genome stability. The error bar denotes the SD from at least three independent experiments. **P < 0.01.