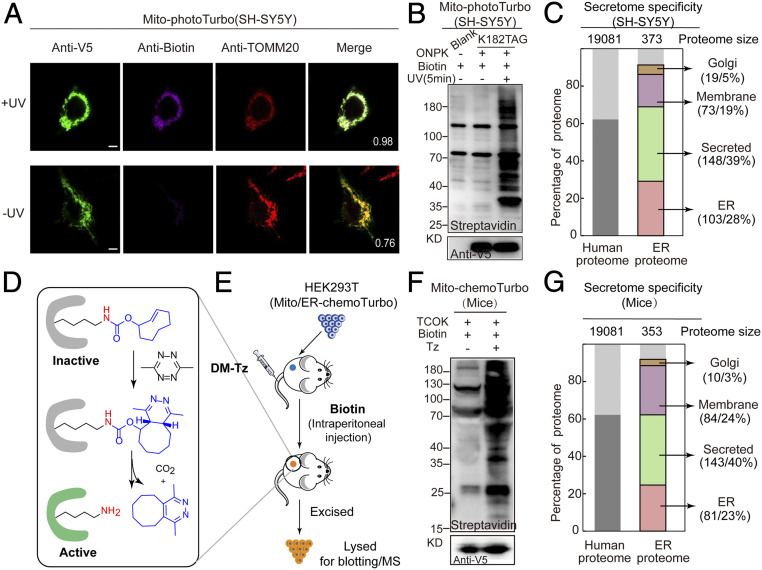
Fig. 5.
Photo/chemoTurbo-enabled subcellular proteomics on neuron culture and living mice. (A) Fluorescence imaging of photoTurbo location and the activation activity in mitochondrial matrix of SH-SY5Y. Anti-V5 (green) was used to visualize Turbo expression, purple is the biotinylation signal to verify the labeling efficiency of photo-controlled Turbo, and red is the mitochondrial marker-TOMM20. UV, 5 min. (Scale bars: 5 µm.) Pearson’s R values of biotin and TOMM20 are shown in the corner. (B) Photo-activation efficiency of photoTurbo for proximity-dependent labeling of proteins in mitochondrial matrix of SH-SY5Y. (C) MS-based identification and quantification of ER lumen proteome labeled by photoTurbo in SH-SY5Y cells. A total of 343 proteins were identified with 92% specificity (∼28% ER resident proteins, 5% Golgi apparatus proteins, 39% secreted proteins, and 19% membrane proteins). (D) Mechanism of the DM-Tz triggered IEDDA for biorthogonal decaging. (E) Schematic illustration of chemo-controlled Turbo activation in living mice. HEK293T cells expressing the mitochondria-Turbo-K182TCOK variant were subcutaneously injected into mice, followed by tail vein injection of DM-Tz and intraperitoneal injection of biotin, which led to the regeneration of active Turbo for proximal labeling. Subsequently, HEK293T cells were excised and lysed before being subject to immunoblotting analysis (F). (G) MS-based identification and quantification of ER lumen proteome labeled by chemoTurbo in mice, which identified 318 proteins (∼23% ER resident proteins, 3% Golgi apparatus proteins, 40% secreted proteins, and 24% membrane proteins).