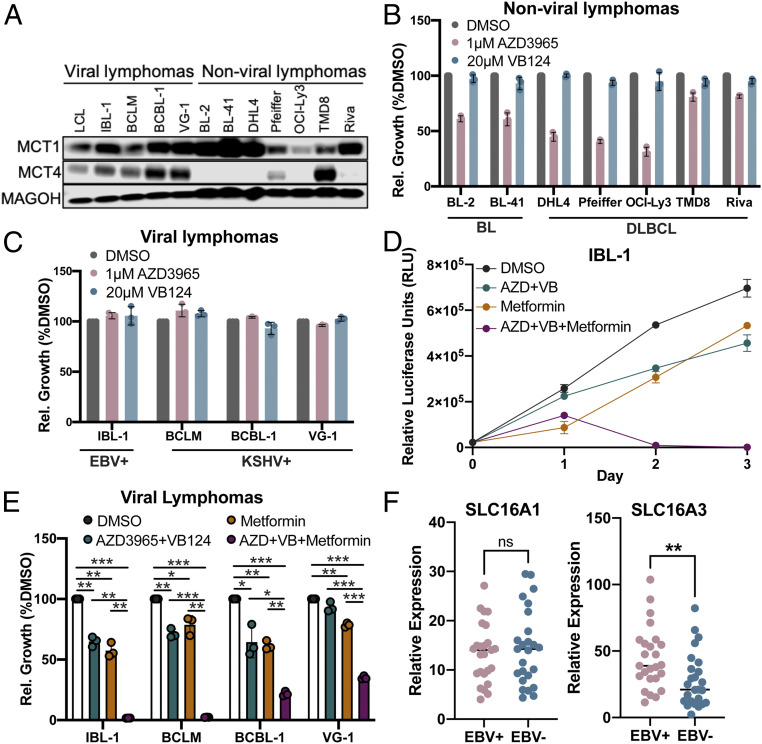
Fig. 7.
EBV+ and KSHV+ lymphoma cell lines are sensitized to killing by metformin upon dual MCT1/4 inhibition. (A) Western blot of MCT1 and MCT4 protein expression in viral (EBV+ or KSHV+) and nonviral (BL or DLBCL) lymphoma cell lines. MAGOH = loading control. (B) Relative cell growth (normalized to DMSO) in nonviral and, in (C), viral lymphoma cell lines. Cell growth was determined by CellTiter Glo luminescence. (D) Growth over time of the EBV + IBL-1 cell line (n = 3), after treatment with DMSO, 1 µM AZD3965 + 20 µM VB124 (AZD + VB), 2 mM Metformin (Metformin), or 1 µM AZD3965 + 20 µM VB124 +2 mM Metformin (AZD + VB + Metformin). The error bars smaller than the line symbols were automatically excluded by graphing software. (E) Relative cell growth of viral lymphoma cell lines at 48 h posttreatment as in D. IBL-1 = EBV+, KSHV− AIDS immunoblastic lymphoma, BCBL-1 = EBV−, KSHV + PEL, VG-1 = EBV−, KSHV+ PEL, BCLM = EBV−, KSHV+ PEL. Statistical significance was determined by a one-tailed paired Student’s t test where *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (F) Relative expression of SLC16A1 (MCT1) and SLC16A3 (MCT4) in EBV-positive (EBV+) and EBV-negative (EBV−) human DLBCL biopsies. RNA-seq comparisons were evaluated by Wilcoxon rank sum test; **P < 0.01, ns (not significant) P ≥ 0.05.