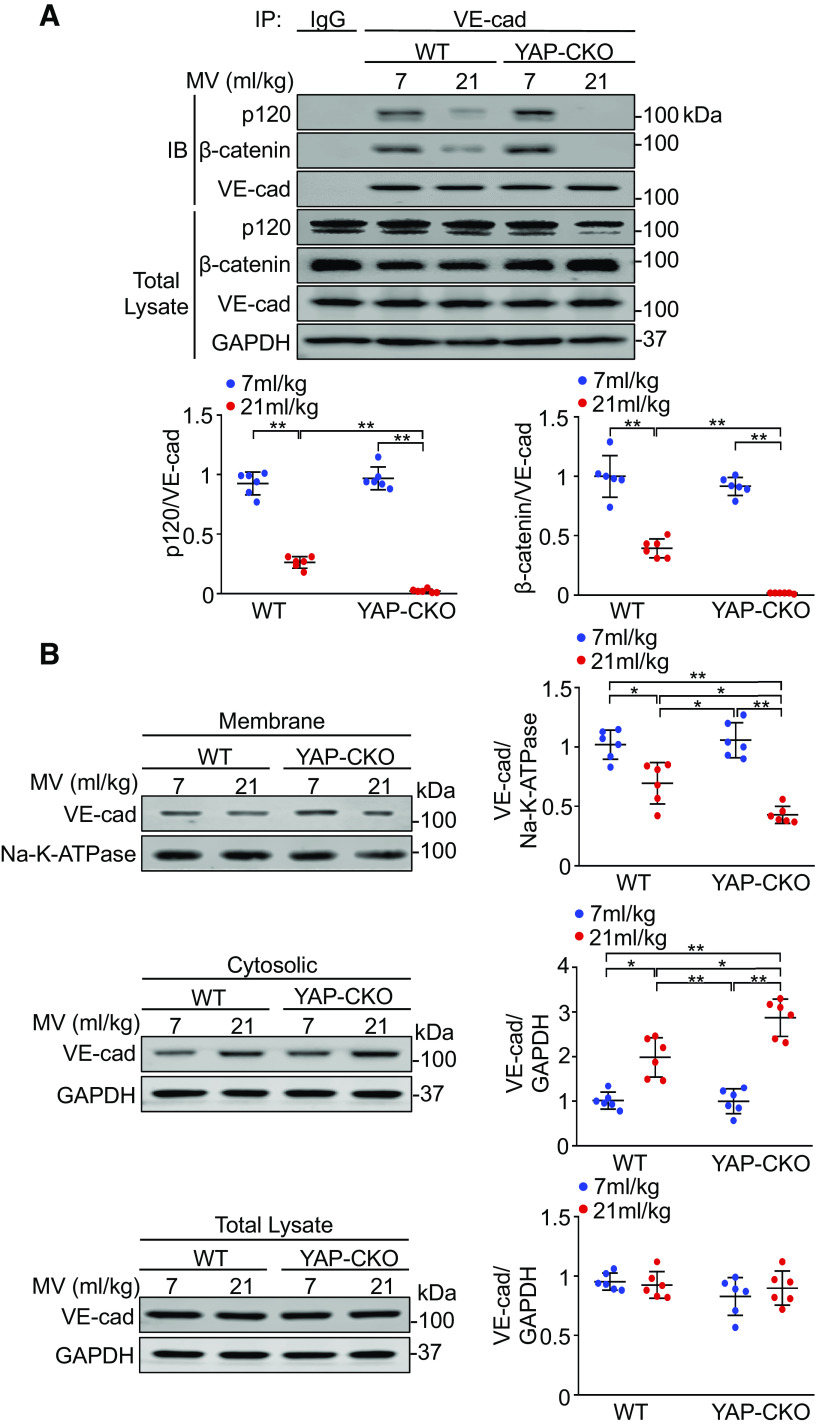
Figure 5.
YAP ablation enhances the disassociation of VE-cadherin (VE-cad) from catenins and VE-cadherin internalization during mechanical ventilation (MV). Wild-type (WT) and endothelial cell-specific YAP knockout mice (YAP-CKO) littermates were ventilated at indicated tidal volumes for 4 h and endothelial cells were isolated from the lung. A: effect of YAP deletion on the association of VE-cadherin (VE-cad) with catenins. Top: the association between VE-cadherin and p120-catenin (p120) or between VE-cadherin and β-catenin was detected by immunoprecipitation with anti-VE-cadherin antibody followed by immunoblotting for anti-p120- and anti-β-catenin antibodies. Bottom: protein quantification (normalized to VE-cad) by densitometry. n = 6 lungs (from 3 male and 3 female mice). **P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. B: effects of YAP depletion on subcellular localization of VE-cadherin. Left: immunoblot showing the levels of VE-cadherin expression in membrane and cytosolic fractions; right: protein quantification by densitometry. Bar graph shows the relative abundance of VE-cadherin protein (normalized to that of loading controls) from six independent experiments (lungs) (from 3 male and 3 female mice). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Data represent means ± SD. YAP, Yes-associated protein.