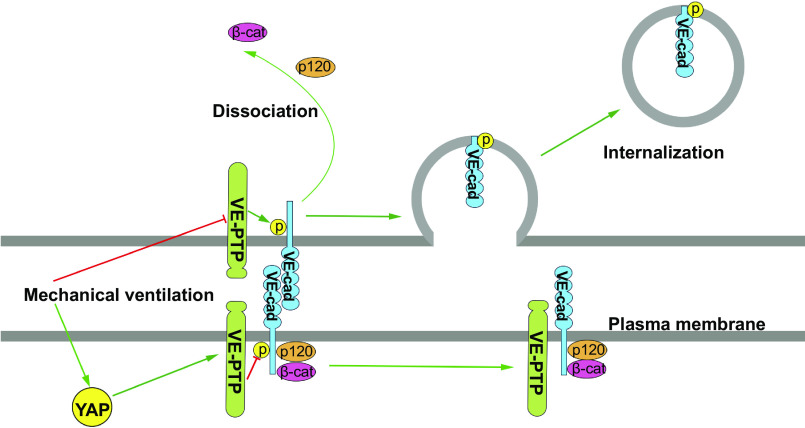
Figure 9.
Model of Yes-associated protein (YAP)-mediated protection against ventilator-induced lung injury. Yes-associated protein (YAP) expression is increased in lung endothelial cells after mechanical ventilation. YAP controls vascular endothelial protein tyrosine phosphatase (VE-PTP) expression, which inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation (p) of VE-cadherin (VE-cad), preventing dissociation of VE-cadherin from p120-catenin (p120) and β-catenin (β-cat), thus stabilizing vascular endothelial barrier function. YAP deletion in endothelial cells causes a decrease in VE-PTP expression, which increases phosphorylation of VE-cadherin, dissociation of p120-catenin and β-catenin from VE-cadherin, and subsequent VE-cadherin internalization from adherens junctions, which leads to enhanced vascular hyperpermeability and neutrophil infiltration.