Figure 4.
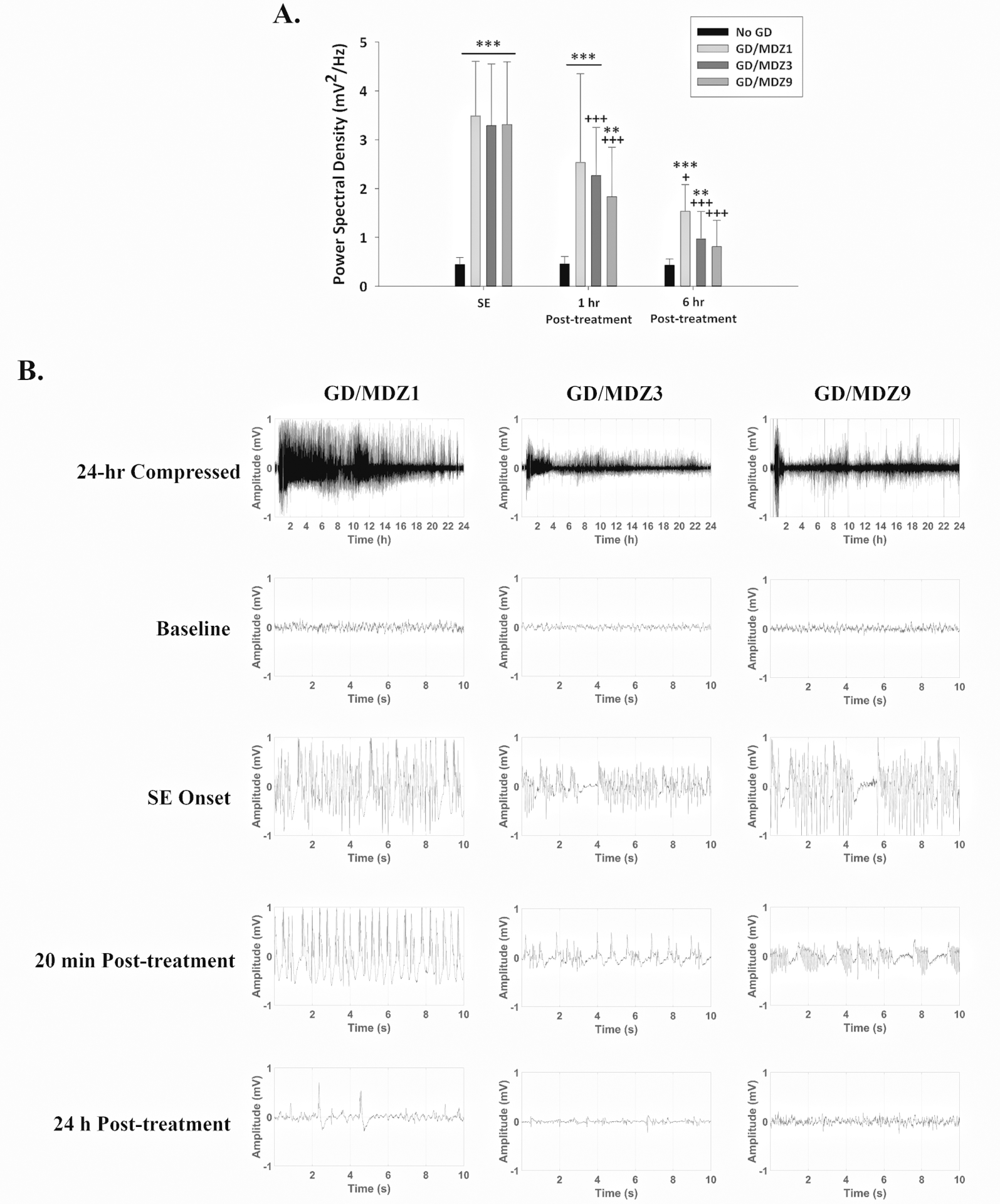
(A) GD (82 μg/kg; SC) exposure increased EEG power spectral density, a marker of seizure severity, during SE, which continued to be increased 1 h after exposure compared with control (No GD; n = 13). Midazolam (3 (GD/MDZ3; n = 19) and 9 (GD/MDZ9; n = 13) mg/kg) reduced EEG power spectral density at 1 and 6 h compared with SE, while 1 mg/kg (GD/MDZ1; n = 5) was only effective at 6 hours. Treatment with 9 mg/kg MDZ reduced EEG power spectral density 6 h after GD exposure and was not significantly different from the No GD control at this time. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01 significantly different from No GD. +P < 0.05, +++P < 0.001 significantly different from SE time point after MDZ treatment. (B) Representative EEG tracings of baseline (prior to GD exposure), the onset of SE, 20 min and 24 h after MDZ treatment.
