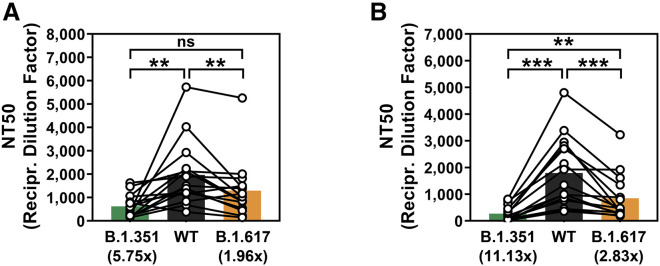
Figure 5.
The S protein of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.617 evades neutralization by antibodies induced upon infection or vaccination with BNT162b2
The S protein of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.617 evades neutralization by convalescent plasma (A) or plasma from BNT162b2-vaccinated individuals (B). S protein-bearing particles were incubated with different plasma dilutions (derived from infected or vaccinated individuals) for 30 min at 37°C before the mixtures were inoculated onto Vero cells. Transduction efficiency was quantified by measuring virus-encoded luciferase activity in cell lysates 16–18 h after transduction and used to calculate the plasma/serum dilution factor that leads to 50% reduction in S protein-driven cell entry (neutralizing titer 50 [NT50]). Presented are the average (mean) data from a single biological replicate (performed with technical quadruplicates). Error bars indicate the standard deviation. Identical plasma samples are connected with lines, and the numbers in brackets indicate the average (mean) reduction in neutralization sensitivity for the S proteins of the respective SARS-CoV-2 variants. Statistical significance of differences between the WT and the variant S proteins was analyzed by paired two-tailed Student’s t test (p > 0.05, ns; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001). See also Figure S3 and Tables S1 and S2.