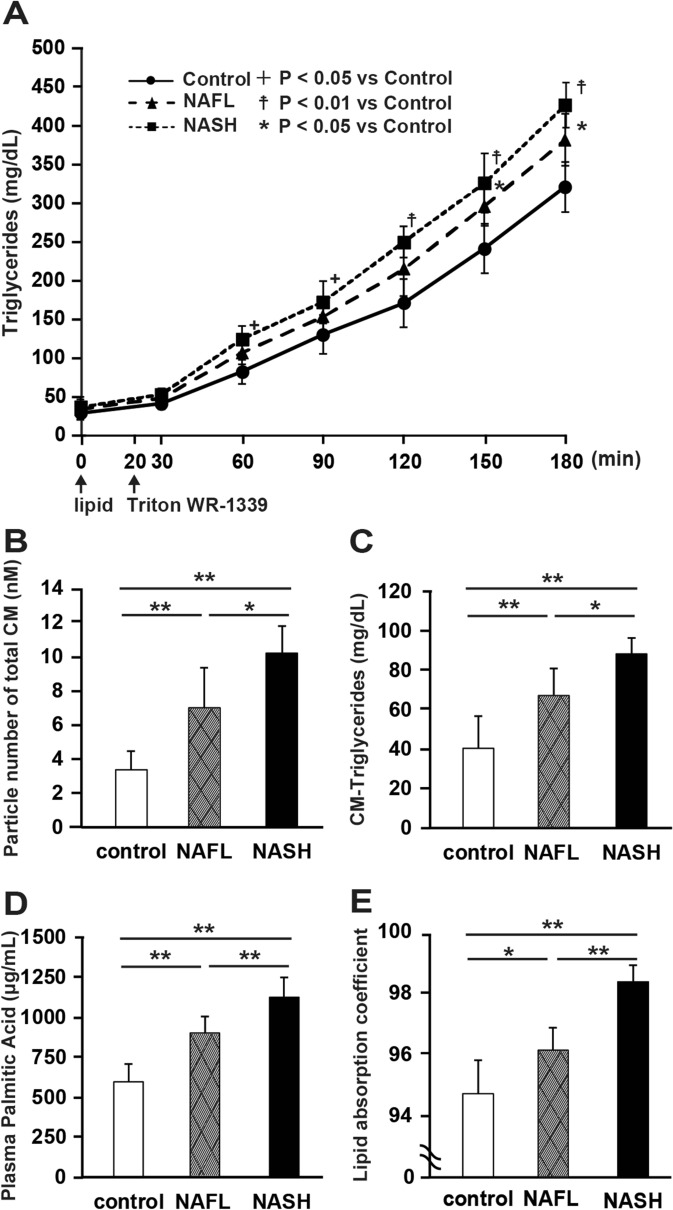
Figure 3.
Increase in lipid and fatty acid absorption in the intestine of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) rats. (A) Time-dependent increase in triglyceride (TG) level in the plasma of each model rat upon infusion of lipid emulsion and Triton (N = 6 per group; + P < 0.05, NASH vs. control; *P < 0.05, NAFL vs. control; ☨P < 0.01, NASH vs. control). Changes in (B) total chylomicron (CM) particle number, (C) chylomicron TG (CM-TG) concentration, (D) palmitic acid concentration before and 180 min after the meal using HPLC and gas chromatography, respectively (N = 6 per group; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). (E) Lipid absorption coefficient (LAC) in each group. LAC was measured when all the three groups of animals were fed the same diet (MFD) (N = 6 per group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). Data in bar plots are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis between the three groups was performed using Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA. Tukey's multiple comparison test was performed only when a significant difference was found.