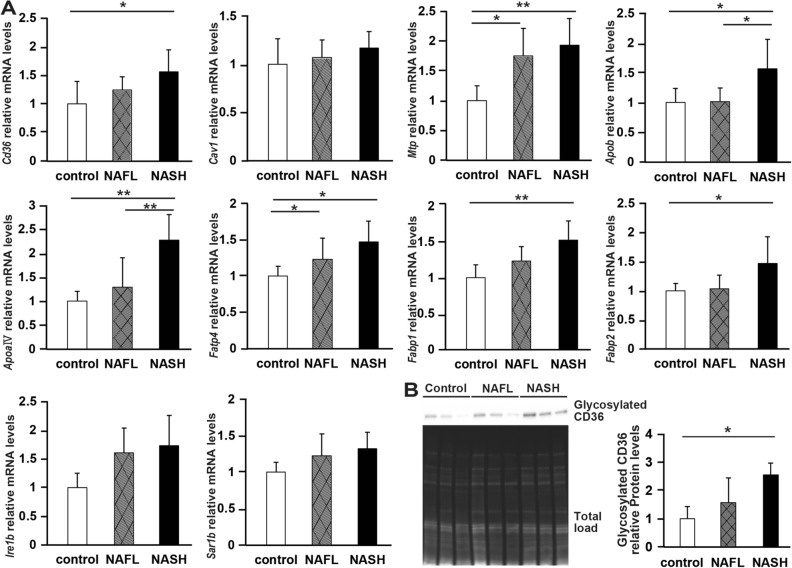
Figure 4.
Expression of genes and proteins involved in fatty acid and lipid absorption in the intestine. (A) The mRNA levels of the following genes were related to the transport of long-chain fatty acids and lipids: cluster of differentiation (Cd36), caveolin 1 (Cav1), microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (Mtp), apolipoprotein B (Apob), apolipoprotein A-IV (Apoa-IV), fatty acid transporter protein 4 (Fatp4), fatty acid-binding protein (Fabp), including liver FABP (Fabp1) and intestinal FABP (Fabp2), inositol-requiring enzyme1b (Ire1b), and secretion associated, Ras-related GTPase1b (Sar1b). N = 6 per group. (B) Western blot analysis of glycosylated CD36 in jejunal tissue. N = 3 per group. Data in bar plots are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical analysis between the three groups was performed using Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA. Tukey's multiple comparison test was performed only when a significant difference was found. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.