Figure 2.
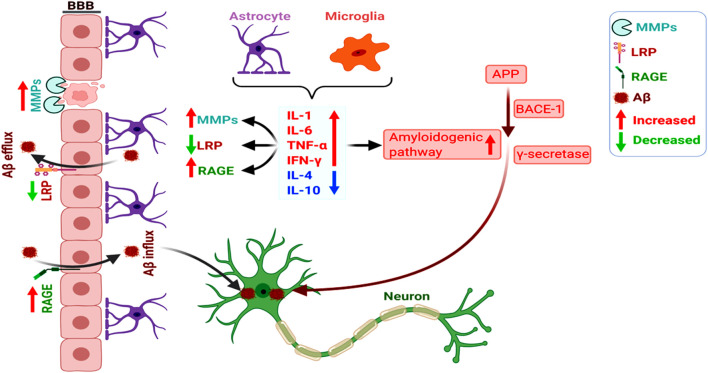
Increased amyloidogenicity, blood-brain barrier (BBB) damage, and dysregulated RAGE and LRP-1 expression induce neuronal Aβ deposition. The pro-inflammatory cytokines (as opposed to anti-inflammatory ones) secreted by the astrocytes and microglia promote the amyloidogenic pathway of APP processing towards Aβ. Glia-mediated inflammation also induces vascular dysfunction involving dysregulated activation of MMPs and altered RAGE and LRP-1-dependent Aβ clearance from the brain, overall increasing neuronal Aβ deposition.