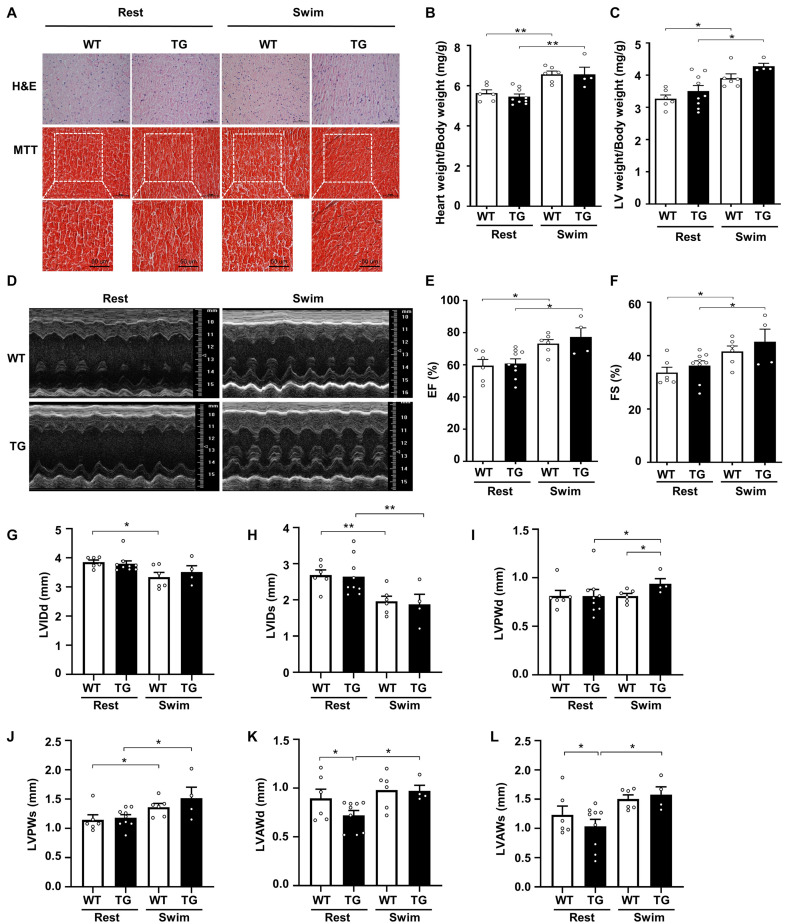
FIGURE 3.
Myocardial CKIP-1 overexpression does not affect physiological cardiac remodeling in response to swimming exercise. (A) CKIP-1 TG mice and WT littermates at 2 months of age were subjected to rest or swimming exercise. Histological sections from hearts were stained with H&E (scale bars, 50 μm) and MTT to detect fibrosis (scale bars, 50 μm). The ratios of heart weight to body weight (B) and LV mass to body weight (C) in WT and CKIP-1 TG mice after swimming exercise. Representative echocardiographic M-mode images (D), ejection fraction (E), and fractional shortening (F) evaluated by echocardiography in anesthetized WT and CKIP-1-TG mice with rest or swimming exercise. (G–L) Transthoracic echocardiography evaluating the left ventricular structure of WT and TG mice following swimming. Values are means ± SEM, n = 4∼9, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01. Statistical differences among groups were analyzed by two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Bonferroni procedure. CKIP-1, casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1; WT, wild type; TG, transgenic; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; MTT, Masson’s trichrome.