FIGURE 2.
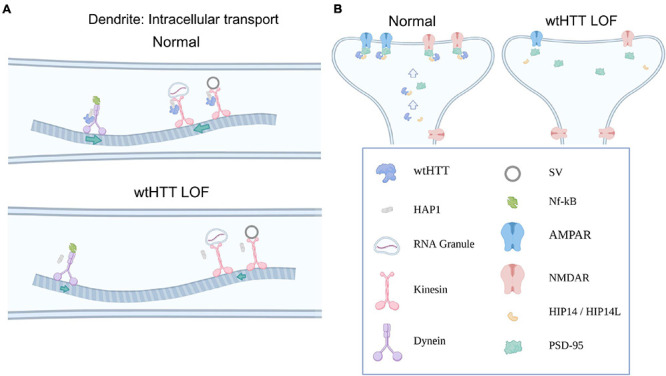
Huntingtin and the postsynapse. (A) Select examples demonstrating how wtHTT positively regulates dendritic transport (top). Through its associations with HAP1, as well as molecular motors, wtHTT regulates anterograde and retrograde transport of synaptic receptors and other cargo in dendrites (left). wtHTT LOF disrupts this transport and slows delivery of synaptic cargo to their respective anterograde or retrograde targets (bottom). (B) Select examples demonstrating how wtHTT positively regulates receptor localization (left). Through its associations with HIP14 and PSD-95, wtHTT regulates synaptic receptor stabilization at the PSD in a healthy postsynaptic neuron. wtHTT LOF disrupts postsynaptic protein clustering and receptor localization (right). Abbreviations: LOF, loss of function; HAP1, huntingtin-associated protein 1; SV, synaptic vesicle; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; AMPAR, α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor; NMDAR, N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor; HIP14/HIP14L, huntingtin-interacting protein 14/huntingtin-interacting protein 14-like; PSD-95, postsynaptic density protein 95. Figure created using Biorender.com.
