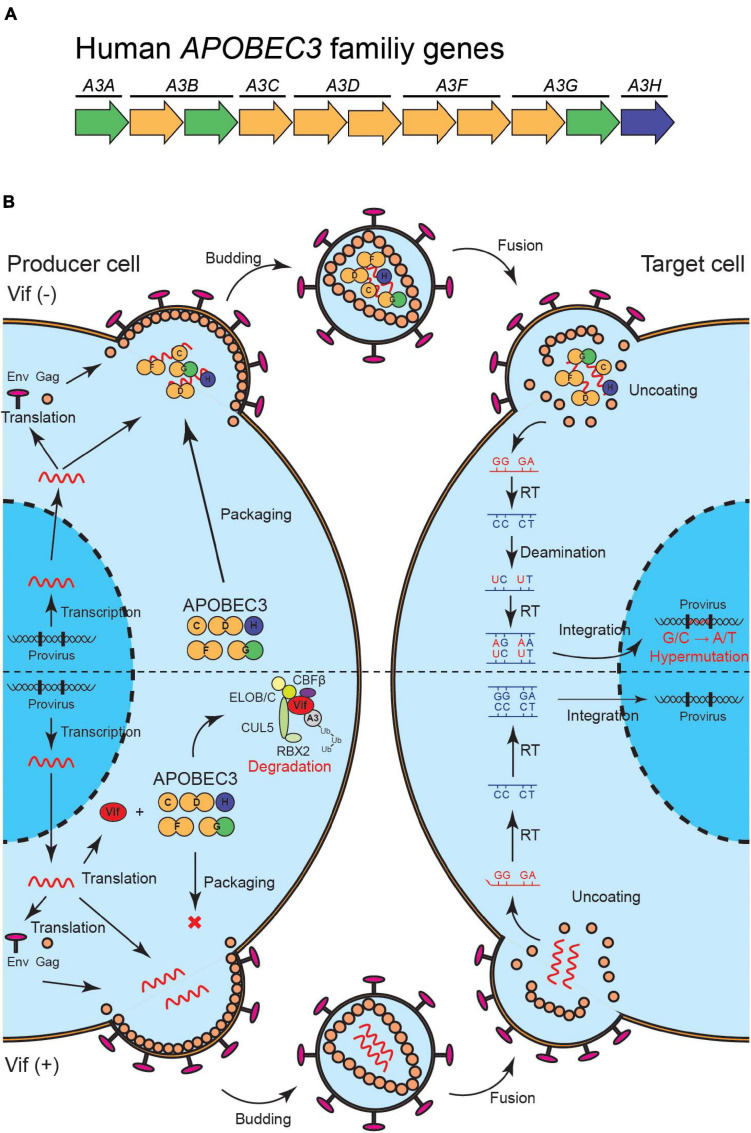
FIGURE 1.
A model of HIV-1 restriction by A3 family proteins and counteraction by HIV-1 Vif. (A) Illustration of human A3 family genes. Human A3 family genes are composed of seven members with one or two zinc-coordinating domains (single of double-domain deaminases); these belong to three phylogenetically different groups, which are shown in green, yellow, and blue. (B) A schematic of HIV-1 restriction by five A3 family proteins and neutralization by HIV-1 Vif. A3C, A3D, A3F, A3G, and A3H are packaged into HIV-1 virions in producer cells and inactivate the virus through cytosine-to-uracil (C-to-U)/guanine-to-adenine (G-to-A) mutations (top). HIV-1 Vif neutralizes the restriction activities of these A3 proteins through proteasome-mediated degradation (bottom). Vif, virus infectivity factor; A3, APOBEC3.