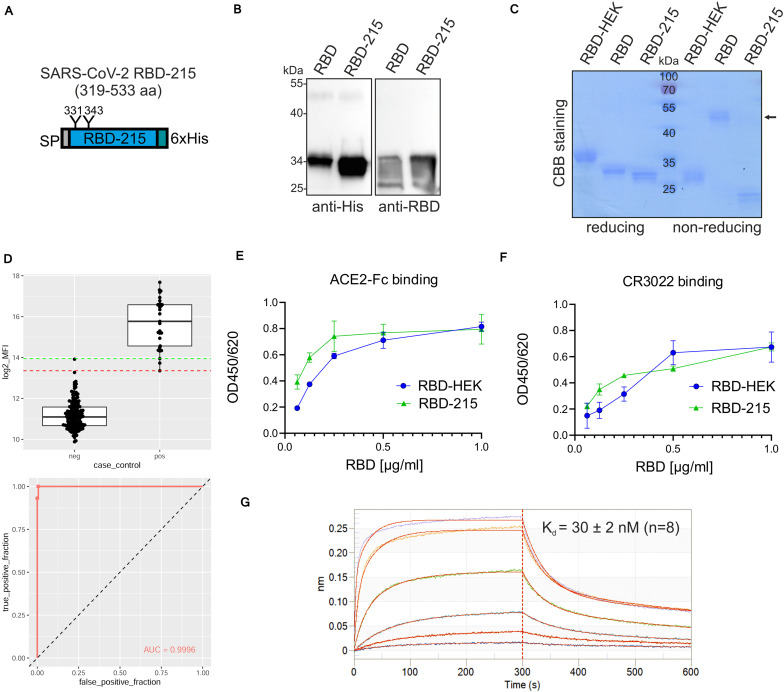
FIGURE 4.
A plant-produced truncated RBD variant is functional. (A) Schematic illustration of the truncated RBD-215 variant. (B) Comparison of RBD and RBD-215 protein expression in leaf extracts of ΔXT/FT Nicotiana benthamiana analyzed by immunoblotting 4 days after infiltration. (C) RBD variants were purified from the apoplastic fluid 4 days after infiltration, analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing or non-reducing conditions, followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) staining. HEK293-produced RBD (RBD-HEK) was included for comparison. The altered mobility of RBD-HEK and the plant produced RBD variant is caused by differences in complex N-glycans. The arrow marks the position of the homodimer. (D) Binding of sera from healthy blood donors collected prior to 2018 (neg, n = 163) and sera from SARS-CoV-2 exposed individuals (pos, n = 26) to plant-produced RBD-215. Binding was analyzed using a Luminex bead-based assay and the median fluorescent intensity (log2 MFI) is shown. The lines indicating the 100% sensitivity cut-off (red) and the 100% specificity cut-off (green) as well as the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) are shown. (E) Binding of purified plant-produced RBD-215 and RBD-HEK to plates coated with ACE2-Fc or (F) antibody CR3022. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (G) BLI analysis. Binding kinetics of the interaction between biotinylated mAb CR3022 loaded on SAX biosensors and RBD-215 at a concentration range of 1.2–300 nM. Representative real-time association and dissociation curves are shown.