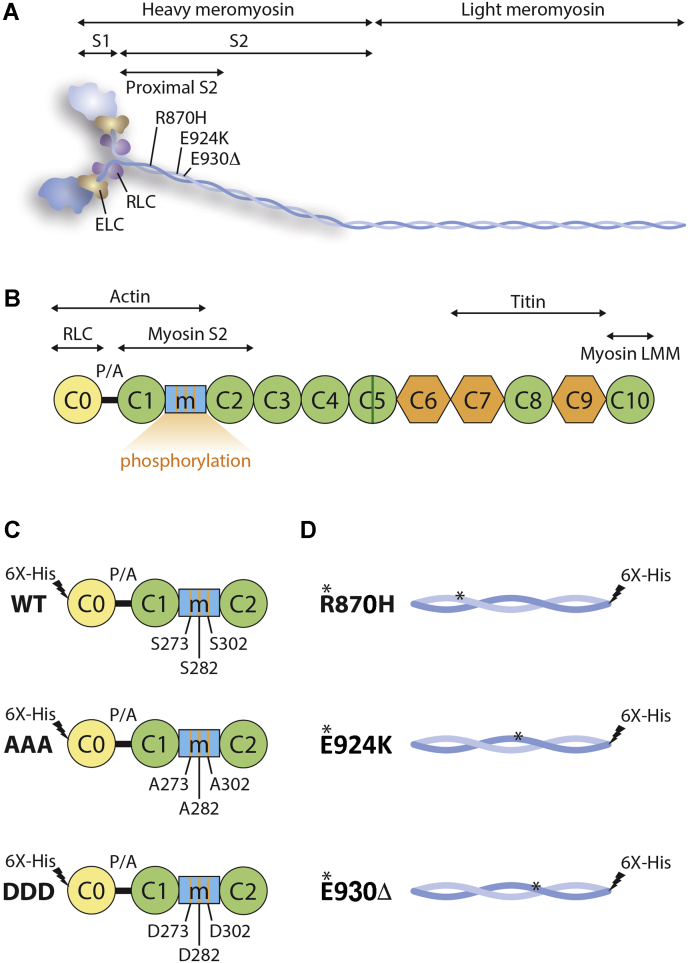
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram demonstrates the association between myosin and cMyBP-C.A, schematic diagram of myosin and cMyBP-C with their interaction domains. Myosin has been divided into N-terminal heavy meromyosin (HMM), which is further divided into S1 and S2 and the C-terminal light meromyosin (LMM). The long helical S2 is marked with proximal region of S2 (126 amino acids), three HCM-causing mutations, R870H, E924K, and E930Δ, and interacting regions with C0-C2 of cMyBP-C. The S1 head of myosin with essential light chain (ELC) and regulator light chain (RLC) proteins. B, in cMyBP-C, the diagram further displays cardiac-specific C0 domain, phosphorylation M domain, and a small inset in C5 domain (green-coded), proline-alanine (P/A)-rich region, interaction region with RLC, immunoglobulin domains from C1-C5, C8, and C10, and fibronectin domains, C6, C7, and C9. The phosphorylated M domain includes three major phosphorylation motifs (Ser-273, Ser-282, and Ser-302) that dynamically regulate the interaction with S2 region of myosin. C, schematic diagram of C0-C2 domains with WT, phospho-ablation (AAA), and phospho-mimetic (DDD), in which the phosphorylation sites Ser-273, Ser-282, and Ser-302 were mutated to either alanine or aspartic acid, respectively. D, proximal S2Wt, and three mutant hS2R870H, hS2E924K, and hS2E930Δ proteins used in the present study. cMyBP-C, cardiac myosin-binding protein-C; hS2E924K, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with E924K mutation; hS2E930Δ, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with E930Δ mutation; hS2R870H, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with R870H mutation; S2, subfragment 2 region.