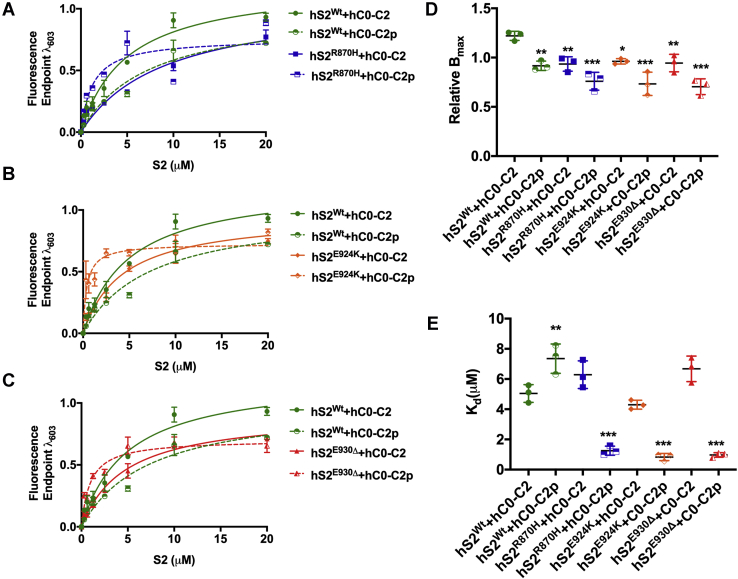
Figure 2.
Mutant hS2 proteins display increased affinity by decreasing Kdto phosphorylated hC0-C2 protein by SPBA. The binding curve between hS2Wt and hC0-C2 (solid green), hS2Wt and hC0-C2p (dashed green), (A) hS2R870H and hC0-C2 (solid blue), hS2R870H and hC0-C2p (dashed blue), (B) hS2E924K and hC0-C2 (solid orange), hS2E924K and hC0-C2p (dashed orange), (C) hS2E930Δand hC0-C2 (solid red), and hS2E930Δand hC0-C2p (dashed red). D, relative maximal binding capacity (Bmax) was determined for each listed combination and compared against hS2Wt and C0-C2 proteins. E, binding affinity or dissociation constant, Kd, compared against hS2Wt and hC0-C2 proteins. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test with single pooled variance. n = 3 with triplicates for each concentration. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. See Table 1 for analysis of main factors and interactions. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus hS2Wt/hC0-C2 controls. hS2E924K, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with E924K mutation; hS2E930Δ, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with E930Δ mutation; hS2R870H, human recombinant proximal S2 protein with R870H mutation; hS2Wt, human recombinant proximal S2 WT protein; S2, subfragment 2 region; SPBA, solid-phase binding assay.