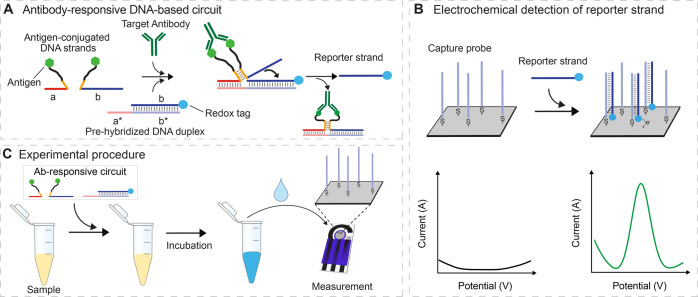
Figure 1.
(A) Antibody-responsive nucleic acid circuit is made of a pre-hybridized duplex DNA containing the redox-labeled reporter and of two antigen-conjugated DNA strands. The binding of the target antibody to the two antigen-conjugated strands induces the formation of a functional complex able to activate a strand displacement reaction that releases the redox-labeled reporter strand from the pre-hybridized duplex. (B) Redox-labeled reporter strand can be detected through an electrochemical platform composed of a silver-based screen-printed disposable electrode on which a complementary DNA capture strand is immobilized. The hybridization of the reporter strand leads to a measurable electrochemical signal using square wave voltammetry (SWV). (C) Schematic of the measuring procedure: the antibody-responsive circuit elements are mixed with the sample of interest and incubated at room temperature (RT) and then transferred onto the screen-printed electrode surface for electrochemical measurement.