Figure 2.
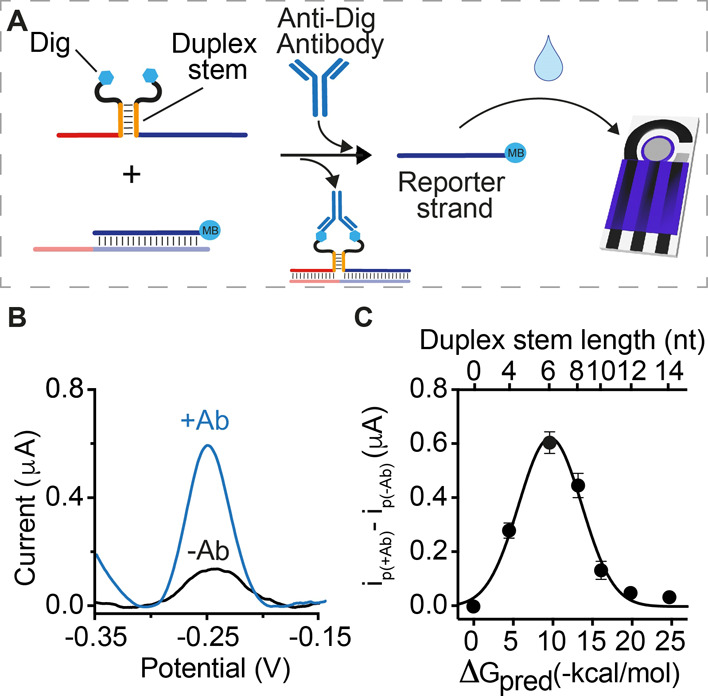
(A) Anti-Dig antibody-responsive circuit was used for signaling optimization. (B) SWV scans obtained in the absence (black) and presence (blue) of anti-Dig antibodies using Dig-conjugated DNA strands with 6-base complementary portions. (C) Plot showing the difference between the electrochemical signals obtained in the presence (ip(+Ab)) and absence (ip(−Ab)) of anti-Dig antibodies with Dig-conjugated DNA strands with variable lengths of the complementary portions. The experiments were performed in a 100 μL phosphate buffer solution (50 mM Na2HPO4, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.0) containing the pre-hybridized DNA duplex (60 nM), Dig-conjugated DNA strands (100 nM each), and anti-Dig antibodies (300 nM). The antibody-responsive circuit was allowed to react for 30 min at RT after antibody addition and then transferred to the disposable electrode surface. SWV scans were performed between −0.35 and −0.15 V at 50 Hz.
