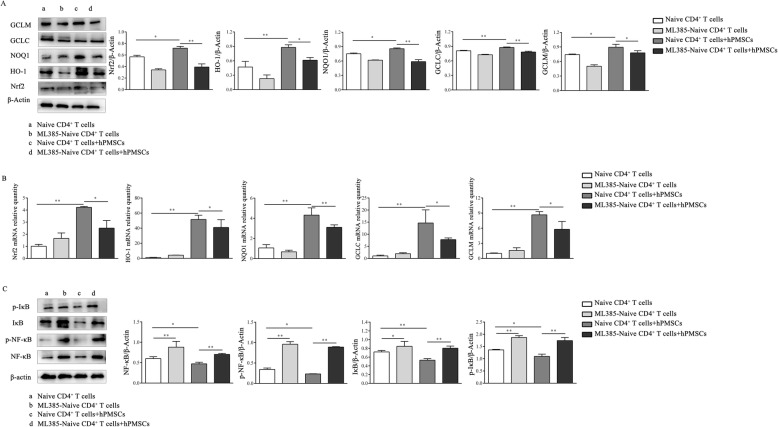
Fig. 6.
hPMSCs induce the differentiation of CD4+IL-10+ T cells by controlling the activation of the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. CD4+IL-10+ T cells were induced, accompanied by changes in IL-2, IL-10, IL-27, and IFN-α2b levels in vitro, by using the naive CD4+ T cells treated with or without the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385 for 12 h, and then naive CD4+ T cells were cultured with or without hPMSCs and collected after 3 days for WB. a WB was performed to determine the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, and GCLM in the different CD4+IL-10+ T cell differentiation systems in vitro. b qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, and GCLM in the different CD4+IL-10+ T cell differentiation systems in vitro. c WB was performed to determine the expression of phosphorylated NF-κB and I-κB in the different CD4+IL-10+ T cell differentiation systems in vitro. The results were obtained from three independent experiments, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01