FIG. 1.
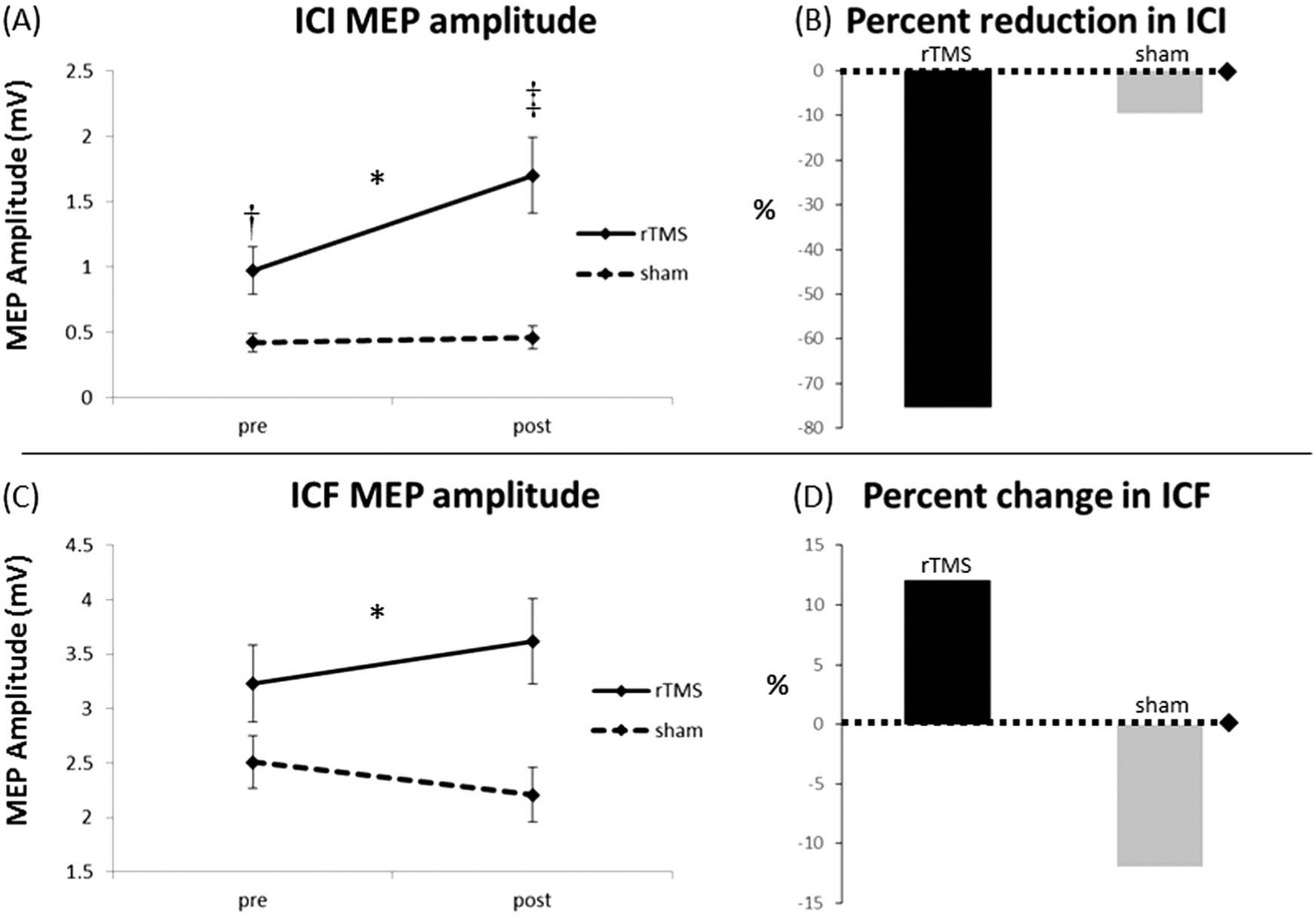
Intracortical inhibition (ICI) and intracortical facilitation (ICF) group results. After repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS), subjects displayed a reduction in ICI (represented as increase in MEP amplitude [A] and as a 75.3% reduction in ICI [B]) that was not observed in subjects who received sham stimulation. We found a significant group-by-time interaction effect with the rTMS group displaying a slight (12.1%) increase in ICF (C, D) and the sham group a slight decrease (12.0%) in ICF from pretesting to posttesting (right panel). *Significant group-by-time interaction effect (P < 0.05). ‡Significant within-group pretest to posttest change (P < 0.01). †Significant between-group difference at pretest (P = 0.01). MEP: motor evoked potential.
