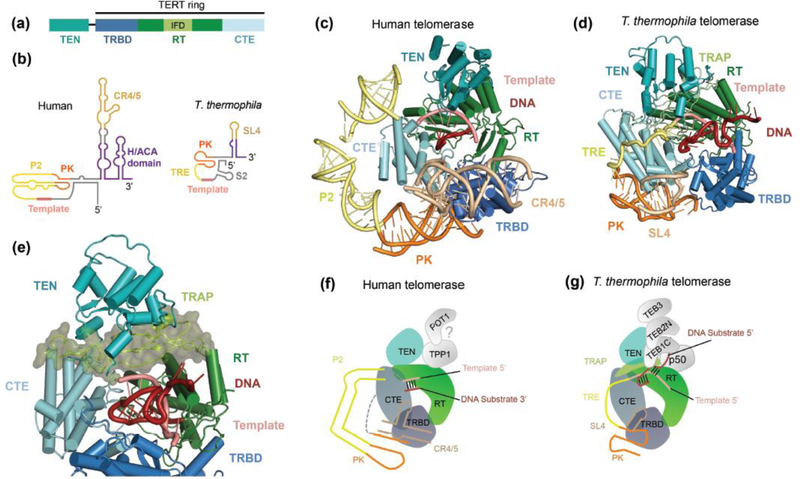
Figure 3.
Structural analysis of the catalytic core of the human and T. thermophila telomerase structures [19,20]. (a) Domain architecture of TERT. The IFD (light green) is embedded in the RT domain (dark green). (b) Secondary structure schematics of human and T. thermophila TERs. RNA domains described in the text are labeled; in addition, T. thermophila stem 2 (S2) is indicated, which is the template 5’ flanking region labeled in Figure 2b. The domain colors shown in (a) and (b) are used for the subsequent panels, which look down into the active site. (c and d) Catalytic cores of human and T. thermophila telomerase, respectively. (e) Close-up view of TRAP in the IFD, highlighted in space-filling representation. (f and g) Schematic representation of the architectures of the catalytic core in human and T. thermophila telomerase, respectively. The positioning of human TPP1 and POT1 is only hypothetical. The interactions observed in T. thermophila telomerase holoenzyme between TERT, p50 and TEB may or may not be paralleled by TERT, TPP1 and POT1 in human telomerase-telomere complexes.