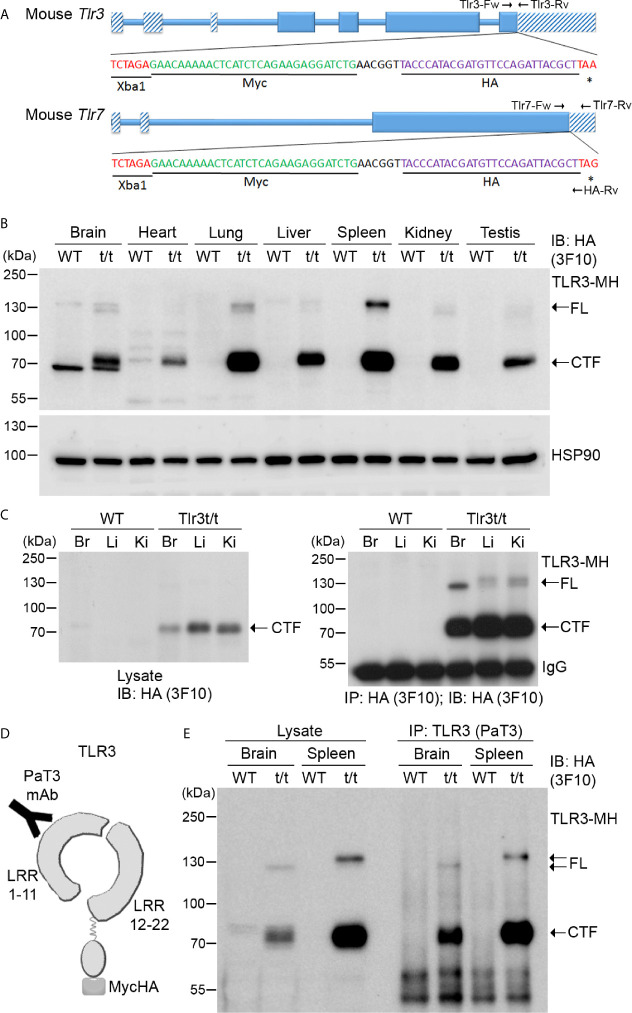
Figure 3.
Dual tagging of Myc and HA cassettes at the C-terminal ends of the Tlr genes reveals expression and processing of TLR. (A) Schematic of the mouse Tlr3 and Tlr7 genes in which a Myc-HA epitope tag has been inserted before the stop codon. Two primer sets, i.e. Tlr3-Fw and Tlr3-Rv for Tlr3 and Tlr7-Fw, Tlr7-Rv and HA-Rv for Tlr7, were used for genotyping the tagged Tlr3 and Tlr7 mice. The results of genotyping are available in Supplementary Figure 2 . *, stop codon. (B) Detection of TLR3-MH protein in multiple tissues of Tlr3t/t mice using immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA antibody (3F10). HSP90 was used as a loading control. (C) Anti-HA antibody (3F10) was used in immunoprecipitation (IP) of TLR3-MH from brain (Br), liver (Li) and kidney (Ki) of WT and Tlr3t/t mice. The IP complex was then analyzed by IB with the same anti-HA antibody. (D) Schematic of TLR3 protein with the C-terminal dual Myc-HA tag. The PaT3 monoclonal antibody recognizes the N-terminal region of TLR3. (E) The N-terminal (NTF) and C-terminal (CTF) fragments of TLR3 remain associated with each other after proteolytic cleavage. TLR3 was precipitated using the PaT3 antibody from brain and spleen lysates of WT and Tlr3t/t mice. The IP complex was then subjected to IB analysis using anti-HA antibody (3F10). FL, full-length TLR3-MH; CTF, C-terminal fragment of TLR3-MH; IgG, immunoglobulin heavy chain.