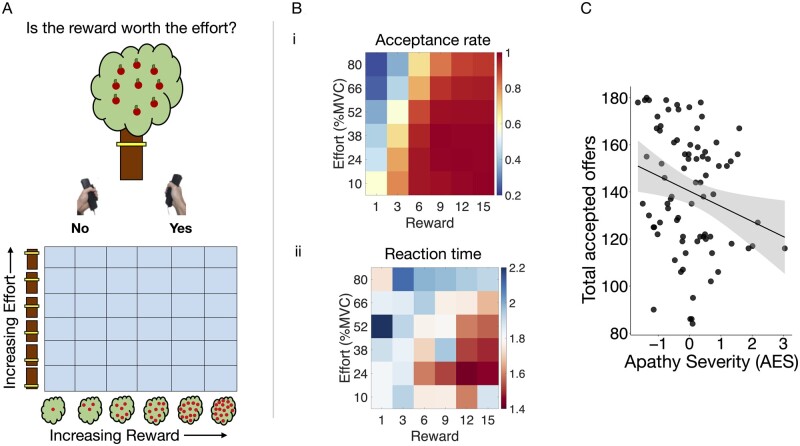
Figure 1.
Effort-based decision making-task and overall performance as a function of apathy. (A) On a trial-by-trial basis, participants were offered monetary rewards (virtual apples) in return for physical effort (height of yellow bar). By varying the amount of reward and effort, their acceptance or rejection of different reward-effort combinations could be mapped in a two-dimensional decision space of reward and effort (6 × 6 grid, bottom). (B) Acceptance rates and reaction times in each section of the decision space. (i) Patients accepted more offers and reacted faster as rewards increased (heat map becomes more red from left to right). (ii) Inversely they rejected more offers and reacted slower as the effort increased (heat map more blue from bottom to top). (C) Fewer offers were accepted overall with increasing apathy severity (z-scored values on x-axis).