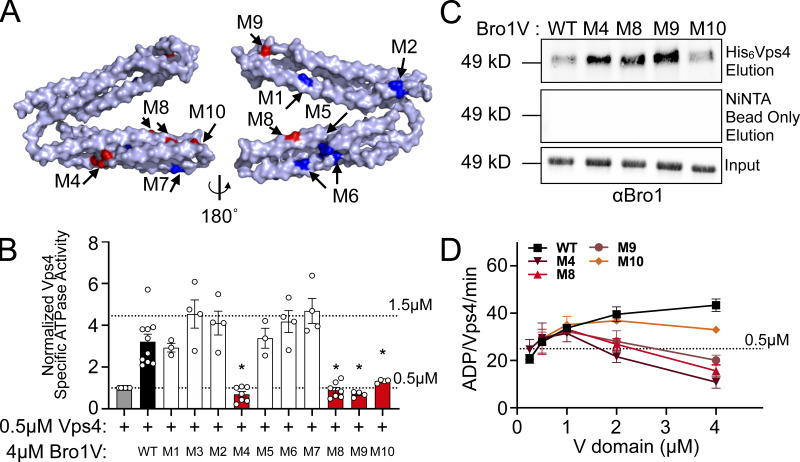
Figure 5.
Bro1 V domain mutations disrupt Vps4 stimulation in vitro without disrupting binding. (A) Model of the V domain based on the S. castellii Bro1 V domain crystal structure (Protein Data Bank accession no. 4JIO, chain A) with amino acid substitution mutations impacting V domain stimulation of Vps4 indicated in red. Conserved residues that when mutated did not impact Vps4 stimulation in vitro are indicated in blue. See Table S4 for individual mutations. (B) Stimulation of Vps4 ATPase activity (0.5 µM) by 4 µM Bro1V(370–709) and Bro1V mutants represented as normalized Vps4 ATPase activity of at least three experiments done in duplicate. Error bars indicate SD, and asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference compared with WT (P < 0.05). (C) Immobilized His6-Vps4 or Ni-NTA beads alone were incubated with Bro1V, Bro1VM4, Bro1VM8, Bro1VM9, and Bro1VM10. Bound material was visualized by immunoblotting with anti-Bro1 antiserum. (D) Vps4 (0.5 µM) ATPase activities with titration of Bro1V, Bro1VM4, Bro1VM8, Bro1VM9, and Bro1VM10 (0.25–5 µM). Vps4-specific activity is expressed as ADP generated per Vps4 molecule per minute. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.