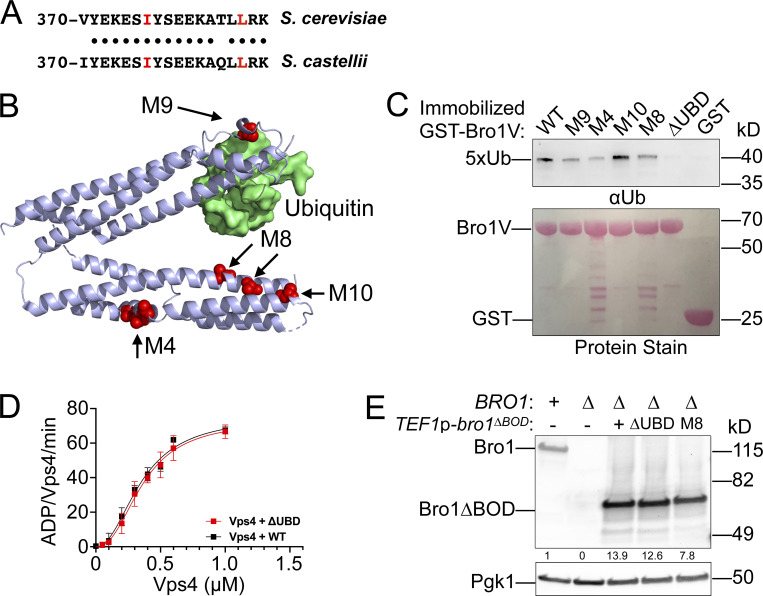
Figure S5.
Bro1V mutants bind Ub. This figure complements Fig. 9. (A) Sequence alignment of V domain aa 370–388 from S. castellii and S. cerevisiae. Conserved amino acids are indicated by black circles, and isoleucine 377 and leucine 386, critical for Ub binding, are highlighted in red. (B) Bro1 V domain mutations M4, M8, and M10 (red) that disrupt V domain stimulation of Vps4 ATPase activity are spatially separated from its Ub-binding site using S. castellii Bro1V crystal structure (Protein Data Bank accession no. 4JIO, chain A). (C) Immobilized GST-fused Bro1V, Bro1VM4, Bro1VM8, Bro1VM9, Bro1VM10, Bro1VΔUBD (I377R) and GST alone were incubated with V5 epitope-tagged linear penta-Ub. Bound material was visualized by both Ponceau S protein stain and immunoblotting for the V5 epitope. (D) Vps4 titrations were performed with 4 µM Bro1V WT or Bro1VΔUBD (L386R). Vps4-specific activity is presented as mean ± SEM. (E) Lysates generated from bro1Δ (GOY65) transformed with empty vector, BRO1, TEF1p-bro1ΔBOD, TEF1p-bro1ΔBOD,ΔUBD (ΔUBD:I377R,L386R) and TEF1p-bro1ΔBOD,M8 plasmids were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against Bro1 and Pgk1. Numbers below the Bro1 blot indicate expression levels normalized to BRO1 expression.