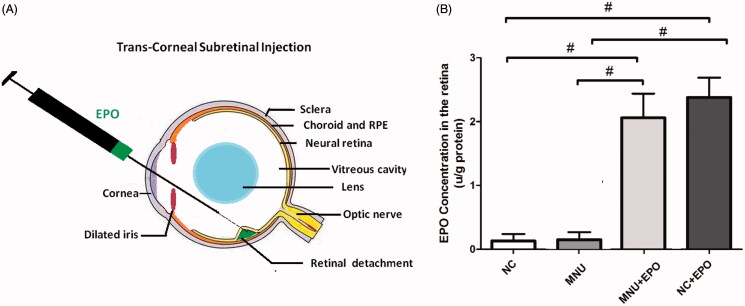
Figure 1.
(A) The subretinal delivery pathway of EPO. A 30½-gague beveled needle was used to make an incision near the corneal limbus. The syringe needle of a Hamilton micro injector was inserted into the anterior chamber through the corneal perforation. The plunger of the Hamilton syringe was slowly pushed to deliver the EPO into the subretinal cavity. A successful subretinal injection would cause one or more retinal blebs on which retinal blood vessels were visible. (B) The retinal EPO level of the treated group was significantly higher than the normal controls. The retinal EPO level of the treated group was also significantly higher than the MNU group. The retinal EPO level of the Normal + EPO group was significantly higher than the normal controls (#p < .01 for differences compared between animal groups; All the values were presented as mean ± SD).