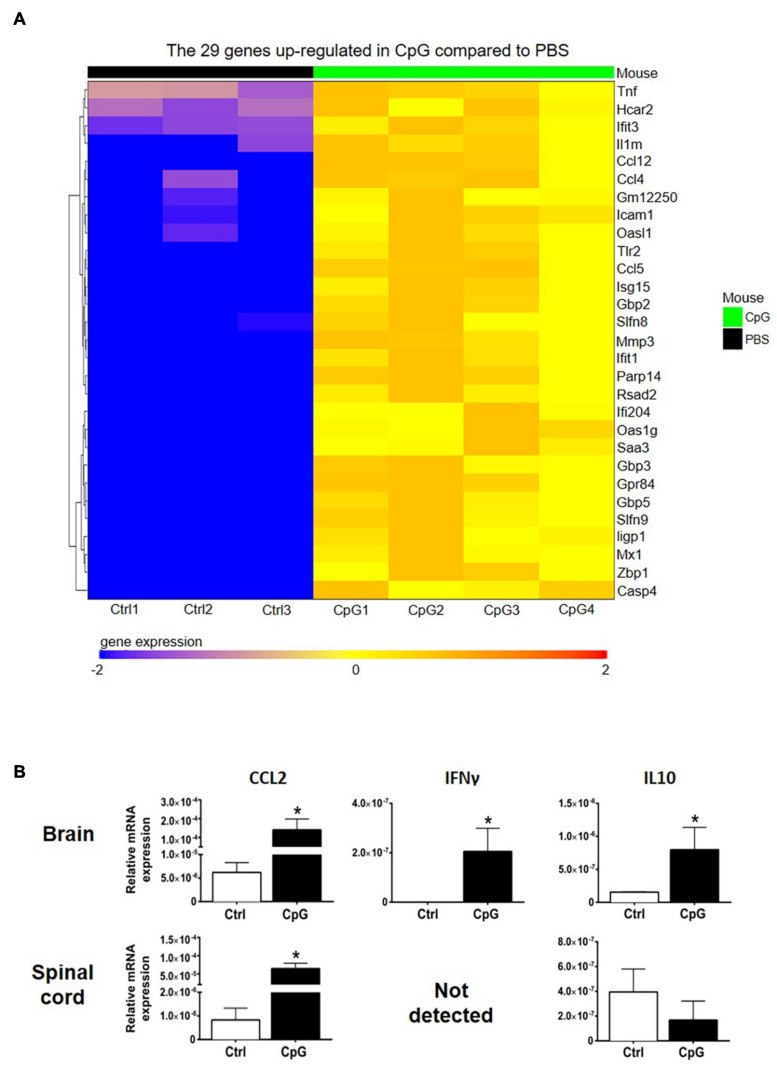
FIGURE 3.
Intrathecal CpG induced inflammation-associated cytokines and chemokines. To investigate how intrathecal CpG influences CNS inflammatory programs in healthy mice, expression of inflammation-associated mediators was analyzed by RNAseq and RT-pPCR. (A) Heatmap of RNAseq analysis of CpG-induced CNS. Intrathecal CpG induced significant upregulation of 29 genes in the brain (LogFC ≥ 2 and adjusted p-value ≤ 0.05). These genes include type I IFN response genes as well as chemokines. (B) Bar graphs show levels of CCL2, IFNγ, and IL10 mRNA in brains and spinal cords 4 h post injection (n = 3–5 per group). Results were analyzed using the two-tailed Mann–Whitney U-test. Data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05.