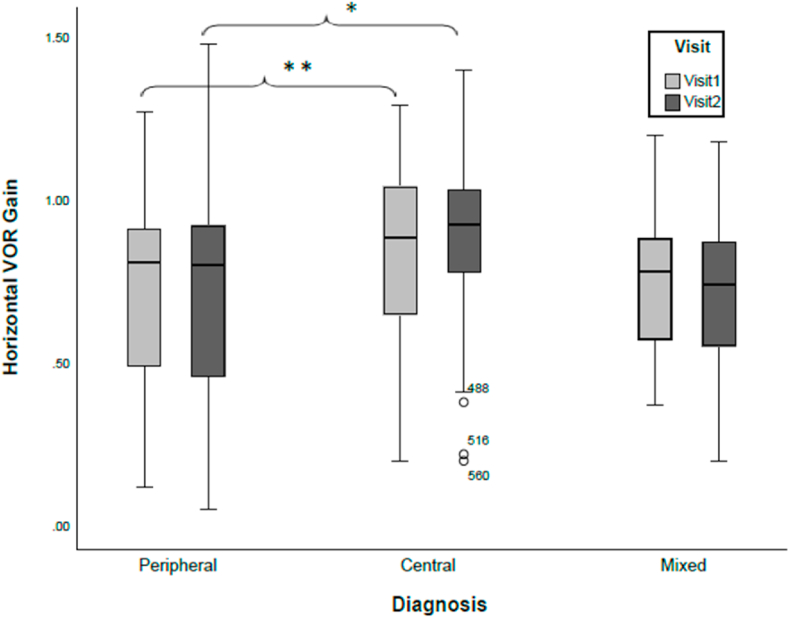
Fig. 2.
Distribution of VOR gain from the horizontal semicircular canal across the three primary diagnostic groups during two visits. Patients with peripheral diagnoses have the largest variability in VOR gain, while the most stability is observed for the patients with central diagnoses (CNS). Significant differences exist between peripheral and central for both visit1 and visit2 (∗ p = 0.002; ∗∗ = p = 0.022). Overall, there is no significant difference in mean VOR gains across the visits for either diagnostic group p < 0.05. Circles represent outliers.