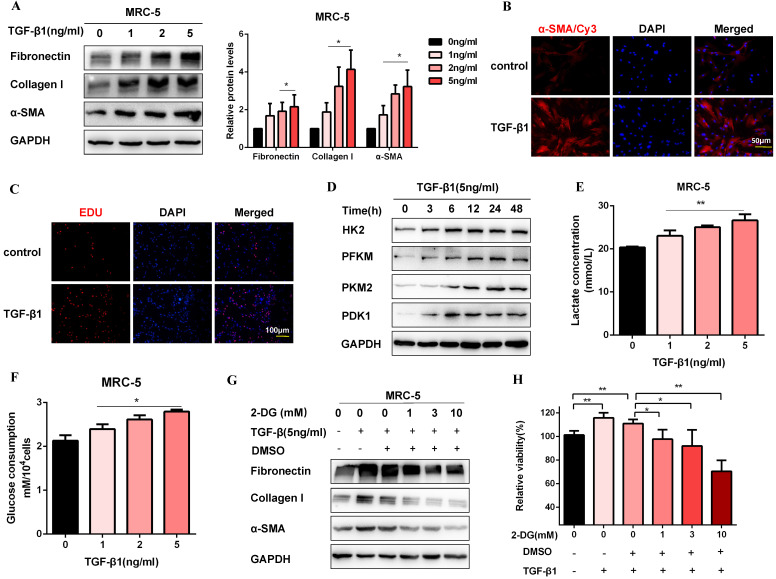
Figure 1.
Glycolysis plays a key role in TGF-β1-induced pulmonary fibroblast activation. (A) Western blot and densitometric analysis of Fibronectin, Collagen I, and α-SMA in MRC-5 cells were treated with 0, 1, 2, 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 48h. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA in MRC-5 cells for the control and TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml) treatment groups. Red represents α-SMA staining; blue represents nuclear DNA staining by DAPI. (C) DNA synthesis was assessed using EDU assay in MRC-5 cells for the control and TGF-β1 (5 ng/ml) treatment groups. Red, EDU; blue, nuclei. (D) Western blot detected levels of HK2, PFKM, PKM2, and PDK1 in MRC-5 cells were treated with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 0h, 3h, 6h, 12h, 24h, 48h. (E-F) MCR-5 cells were treated with 0, 1, 2, 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 for 48 h. Lactate levels and glucose consumption were determined (n = 3), with *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. the control group. (G-H) MRC-5 cells were pretreated with 2-DG (1 mM, 3 mM, 10 mM) for 1 hour, followed by TGF-β1 treatment for 48 hours. Fibronectin, Collagen I, and α-SMA expression were determined by western blot, and cell viability was detected by MTT assays (n = 3), **P < 0.01.