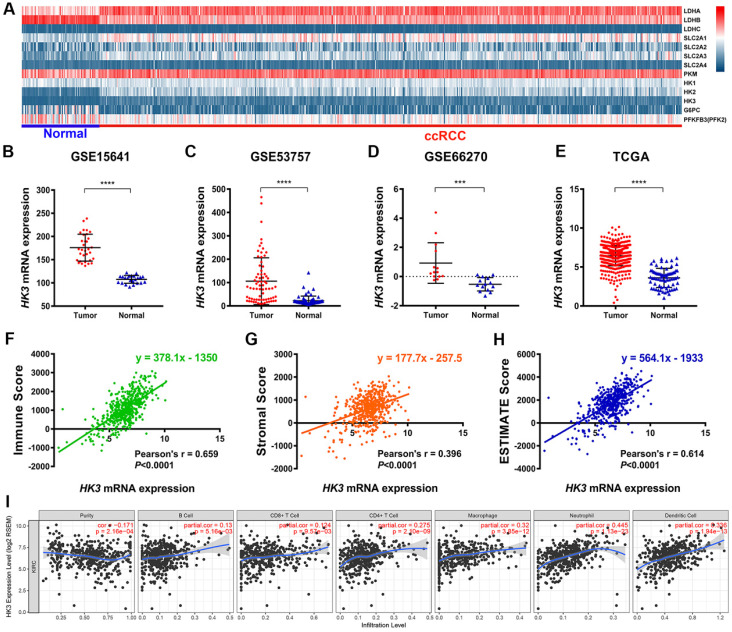
Figure 1.
Identification of the differential HK3 expression in ccRCC and normal samples and its correlation with immune cell infiltration based on multiple cohorts. (A) Differential expression analysis of hub genes related to the glycolysis signaling pathway, including HK1-3, LDHA-C, SLC2A1-4, PKM, G6PC, and PFKFB3, between ccRCC tissues and adjacent normal tissues in 533 ccRCC patients from the TCGA cohort. (B-D) Differential HK3 expression was observed in 118 ccRCC primary tumors, in comparison with the adjacent normal tissues from GSE15641 (32 ccRCC samples), GSE53757 (72 ccRCC samples), and GSE66270 (14 ccRCC samples), as per Student's t-test. (E) The transcriptional expression levels of HK3 were significantly high in 533 ccRCC tissues, compared with 72 normal tissues in the TCGA-KIRC cohort. (F-H) Spearman's correlation indicated a relationship between HK3 and the immune contexture, stromal contexture, and the tumor purity of the ccRCC microenvironment, using ESTIMATE algorithm. (I) The association between the abundance of infiltrating immune cells and HK3 expression was analyzed.